10 biggest cybersecurity threats facing US businesses

The 10 biggest cybersecurity threats account for $8.6 billion in business losses. Find out which cyber incidents pose a risk to your business
The rapid pace of technological advancements and digital transformation has given rise to more complex and dangerous cybersecurity risks. And as these threats grow and evolve, insurers and businesses need to know what they’re up against.
In this article, Insurance Business delves deeper into the biggest cybersecurity threats facing businesses in the US. We will crunch the numbers to get a clear picture of the scope and financial impact of each.
Insurance professionals and business owners can use this guide to gain a deeper understanding of how cyber risks can affect their operations. They can also get expert tips on how to protect themselves from damaging cyberattacks.
Cyber threats come in different forms. From malicious software to social engineering scams, cybercriminals are using more devious tactics to infiltrate computer systems. Here are the biggest cybersecurity threats facing US businesses based on the Federal Bureau of Investigation’s (FBI) latest internet crime report. The list is arranged by business losses.
1. Investment fraud
Total losses: $4.57 billion
Number of complaints: 39,570
Investment scams are designed to entice victims with the promise of huge returns on their investments. Investment fraud has consistently been on the top of the FBI’s list of the biggest cybersecurity threats in terms of losses in the past several years.
Last year, such incidents resulted in $4.6 billion in losses, rising more than a third from $3.3 billion in 2022. Investment scams involving cryptocurrency comprise most of the 39,570 recorded complaints. The losses amounted to almost $4 billion in 2023, up from $2.6 billion from the previous year.
2. Social engineering
Total losses: $2.95 billion
Number of complaints: 21,489
In social engineering, cybercriminals use emotional and psychological tactics to manipulate a victim into taking a desired action. This type of cyberattack uses powerful motivators such as money, love, fear, and status to get sensitive information.
Attackers then use the stolen data to extort a company or gain a competitive advantage. The use of emotions to trick people makes social engineering one of the biggest cybersecurity threats for businesses in the US.
Social engineering attacks take on many forms. Among the most common is business email compromise (BEC). In a BEC attack, bad actors assume the identity of a trusted individual to trick users into sharing data or sending money.
The FBI received almost 21,500 complaints of BEC attacks in 2023. These incidents cost businesses a whopping $2.9 billion in losses.
3. Data breach
Total losses: $534.38 million
Number of complaints: 3,727
Data breaches happen when cybercriminals get unauthorized access to confidential information. Incidents of data breach have been increasing in the past few years, according to FBI’s data. From around 1,290 in 2021, the number of complaints rose to almost 2,800 in 2022 before hitting about 3,730 last year.
In terms of losses, data breaches have cost businesses around $534.4 million, up 16% from $459.3 million in 2022.
4. Government impersonation
Total losses: $394.05 million
Number of complaints: 14,190
This occurs when cybercriminals impersonate a government official to collect money. The FBI reported 14,190 complaints of government impersonation scams in 2023. These incidents have resulted in over $394 million in losses, ranking as the third costliest cybersecurity threat on the list. This figure is up 63% from $240.5 million in 2022.
5. Identity theft
Total losses: $126.2 million
Number of complaints: 19,778
What makes identity-driven attacks one of the biggest cybersecurity threats? They are difficult to detect. In this type of cyberattack, bad actors steal a valid user’s credentials and masquerade as that user.
Here are some of the most common forms of identity-based attacks:
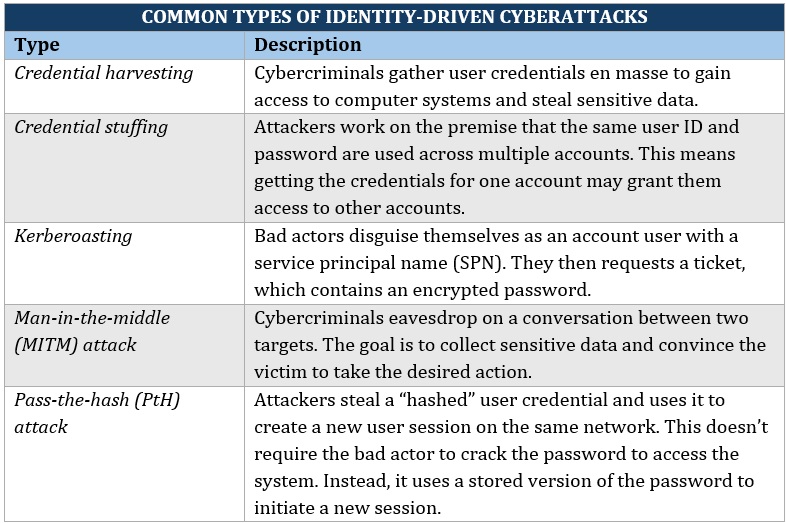
There were almost 19,800 incidents of cyber-related identity theft reported to the FBI last year. These account for about $126.2 million in losses. Although the value is astounding, this is actually a 55% decline in the past two years.
Recently, we unveiled our five-star awardees for the Top Cyber Insurance Companies in the USA. By partnering with these insurers, you can be sure that you’re in good hands if you become the target of a cyberattack.
6. Ransomware
Total losses: $59.64 million
Number of complaints: 2,825
Ransomware is a type of malware that cybercriminals use to prevent a victim from accessing essential files or systems until a ransom is paid. In a ransomware attack, bad actors encrypt the victim’s data and offer a decryption key in exchange for payment.
Ransomware is often launched through malicious links sent in phishing emails. Systems may also be encrypted through policy misconfigurations and unpatched vulnerabilities.
In 2023, ransomware attacks cost more than $59.6 million in losses from 2,825 reported incidents. This amount doesn’t include lost time, wages, and equipment, as well as restoration costs.
7. Denial-of-service attacks
Total losses: $22.42 million
Number of complaints: 540
A denial-of-service (DOS) attack works by flooding a network with false requests to disrupt a business’ operations. When a DOS attack occurs, the victims will not be able to perform routinary tasks, including accessing emails and websites.
This type of cybersecurity threat doesn’t often result in stolen data and can be resolved without paying a ransom. But they can cost companies time and resources to restore operations.
DOS attacks are categorized under botnets in FBI’s data. The organization received 540 complaints last year. These incidents resulted in $22.4 million in losses, up from $17.1 million from the previous year.
8. Phishing & spoofing
Total losses: $18.73 million
Number of complaints: 298,878
Phishing and spoofing schemes are designed to trick users into providing sensitive information to scammers. Although both involve deception, there’s a distinction between these cybersecurity threats.
Phishing uses email, SMS, social media, and social engineering tactics to lure a victim into sharing confidential information or downloading a malicious file on their devices. Phishing takes on several forms, including:
- spear-phishing: targets specific individuals or organizations through malicious emails
- smishing: uses fraudulent text messages to trick victims into sharing sensitive data
- vishing: uses fraudulent phone calls and voice messages to convince victims to disclose private information
- whaling: targets senior or C-level executives to steal money or information, or gain access to their computer to execute further cyberattacks
Spoofing happens when bad actors try to convince a victim that they are interacting with a trusted source. Cybercriminals often disguise an email address, sender, phone number, or website URL as something legitimate by changing a character.
The FBI received almost 299,000 phishing and spoofing complaints last year. Although the figure is down 7% from the previous year, these types of attacks remain the biggest cybersecurity threats in the country.
In terms of losses, phishing and spoofing attacks account for $18.7 million in 2023. This is a huge drop from $160 million in 2022.
9. Copyright infringement
Total losses: $7.56 million
Number of complaints: 1,498
Copyright infringement is the illegal use of others’ intellectual property. This ranges from trade secrets and proprietary products to music, movies, and even computer software. There were about 1,500 reports of intellectual property rights infringement last year. These violations cost businesses more than $7.5 million.
10. Malware
Total losses: $1.21 million
Number of complaints: 659
Malware, short for malicious software, is any program or code created to harm a computer, network, or server. The goal is to steal sensitive data and disrupt a business’ operations.
This type of cyberattack tricks users into downloading what seems to be harmless files or links. If successful, these programs enable bad actors to access not only the victim’s computer but also the entire network within a company.
Malware is the most common form of cybersecurity threat, primarily because it comes in many forms. These include ransomware, which is also part of the list. Other examples are adware, spyware, trojan, and worms.
There were 660 incidents of malware reported to the FBI last year. These amount to $1.2 million in losses. The figures exclude ransomware.
The FBI’s internet crime report recorded around $12.5 billion worth of losses from almost 692,000 reports of cyber incidents. The 10 biggest cybersecurity threats on our list account for more than two-thirds or $8.6 billion of the monetary losses.
With the constantly evolving threat landscape, cybercrime losses are predicted to reach $10.5 trillion globally by 2025. This highlights the importance of having solid cybersecurity measures for all businesses.
One of the biggest misconceptions about cybersecurity threats is that you have to be a large corporation in America to be vulnerable. This belief leaves many small businesses unprepared once they have become targets.
There are several practical ways, however, for small and mid-size enterprises to protect themselves without the need to deplete their resources. Here are some suggestions from the US Small Business Administration (SBA).
1. Assess your cyber risks
Businesses need to have a deep understanding of the risks they’re facing. A cybersecurity risk assessment can help them identify their vulnerabilities and help them create a plan of action. This can include user training, guidance on securing email platforms, and advice on protecting business’ information.
2. Invest in employee training
Employees and emails have become a leading cause of data breaches because they provide a direct path into the business’ computer systems. Training staff in basic cybersecurity best practices can go a long way in preventing cyberattacks.
3. Keep antivirus software updated
Businesses must ensure that their systems are equipped with the latest antivirus software and antispyware. They must also keep these programs regularly updated.
4. Make sure networks are secure
Businesses can safeguard their internet connection by using a firewall and encrypting all their data. Companies must also ensure that their Wi-Fi networks remain hidden and secure.
5. Use strong passwords
One of the simplest ways to improve cybersecurity is to use strong passwords. A strong password has:
- 10 characters or more
- at least one uppercase letter
- at least one lowercase letter
- at least one number
- at least one special character
6. Activate multi-factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a verification process that requires users to provide two or more proofs of their identity to access their accounts. This adds another layer of security. For example, businesses can require users to provide a password and a code sent to a different device before granting them access to an online account.
7. Conduct regular data back-ups
One of the most cost-effective cybersecurity measures, backing up data ensures that essential information can be recovered if a cyberattack or computer issues occur.
8. Ensure payment processing is secure
Businesses should work with their banks to make sure that the most trusted and validated tools and anti-fraud services are being used. Companies must also isolate payment systems from less secure programs. They should use separate computers when processing payments and surfing the internet.
9. Control physical access
Companies should prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing or using business-owned computers. They should also grant administrative privileges only to trusted IT staff and key personnel.
10. Get cyber insurance
Cyber insurance helps cover the financial losses resulting from a cyber incident. It can also pay for claims made by individuals or groups that may have been harmed due to an attack on the business.
If you’re searching for a cyber insurance provider that offers the best coverage, our Best in Insurance Special Reports page is the place to go. You can be assured of the highest levels of service and support from these companies if faced with a cybersecurity threat.
Have you experienced being targeted in a cyberattack? How did cyber insurance help? We’d love for you to share your story below
Keep up with the latest news and events
Join our mailing list, it’s free!




