7 Cloud Computing Trends (2024-2029)

You may also like:
Cloud computing has been one of the most critical technologies of the last decade.
Approximately 100 zettabytes of data will be stored in the cloud by 2025.
And we are still seeing many breakthroughs in this space.
So, what are some of the more important advancements in cloud computing?
Read this list of seven trends to see where this industry is headed in the future.
1. Cloud Computing Goes To The Edge
Edge computing is a framework in which data is stored and processed as close to the original device as possible.
Searches for “edge computing” have grown by 28% in the last 5 years.
In traditional cloud computing frameworks, data travels from the device to the data center and back.
Waiting for data to make this “journey” is what causes latency.
And edge computing’s main selling point is that it reduces latency because data is processed right where the data is being generated.
One significant driver of this trend is the seemingly ever-growing number of IoT devices.
Estimates show that there will be approximately 27 billion IoT devices by 2025. These devices will produce over 50 zettabytes of data.
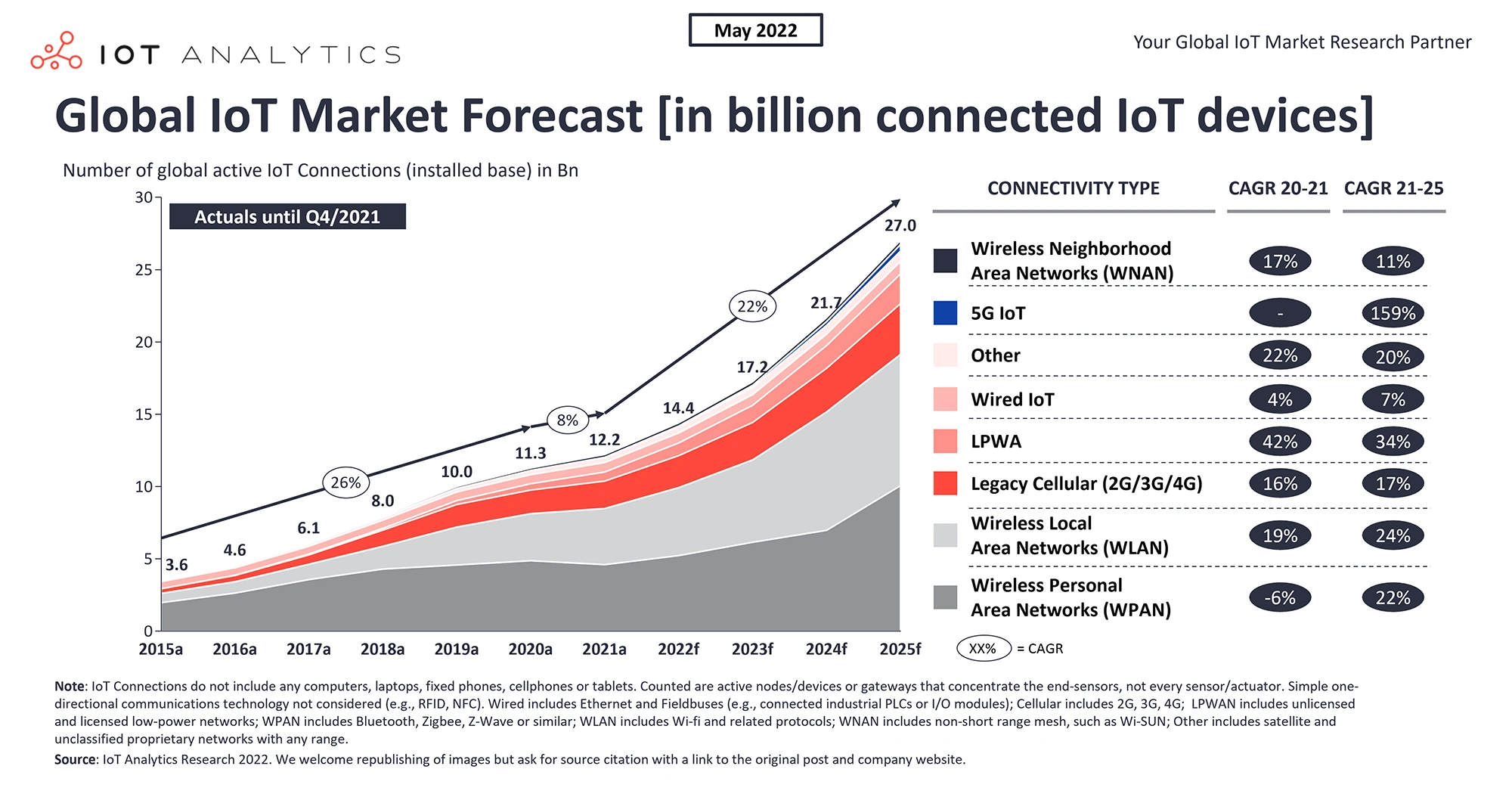
Number of IoT devices from 2015 to 2025.
Edge architecture handles this flow of data more effectively than other solutions (at a latency rate of 1 millisecond).
Additionally, because this framework mitigates the need for data to travel long distances, it also helps secure devices from cyberattacks.
Gartner estimates that organizations that isolate and segment their networks through an edge architecture will experience 25% fewer successful cyberattacks.
These benefits are crucial reasons behind rising edge computing adoption rates among businesses.
Overall, spending on edge computing will reach $317 billion by 2026, up from $208 billion in 2023.
2. Cloud Gaming Becomes More Mainstream
Cloud gaming is a method of playing video games hosted on remote servers.
In traditional gaming, video games are hosted and run locally on the playing device (PC, console, mobile, etc.).
In cloud gaming, video games are hosted and run remotely on a cloud server. And the user streams the video game on their device through the internet.
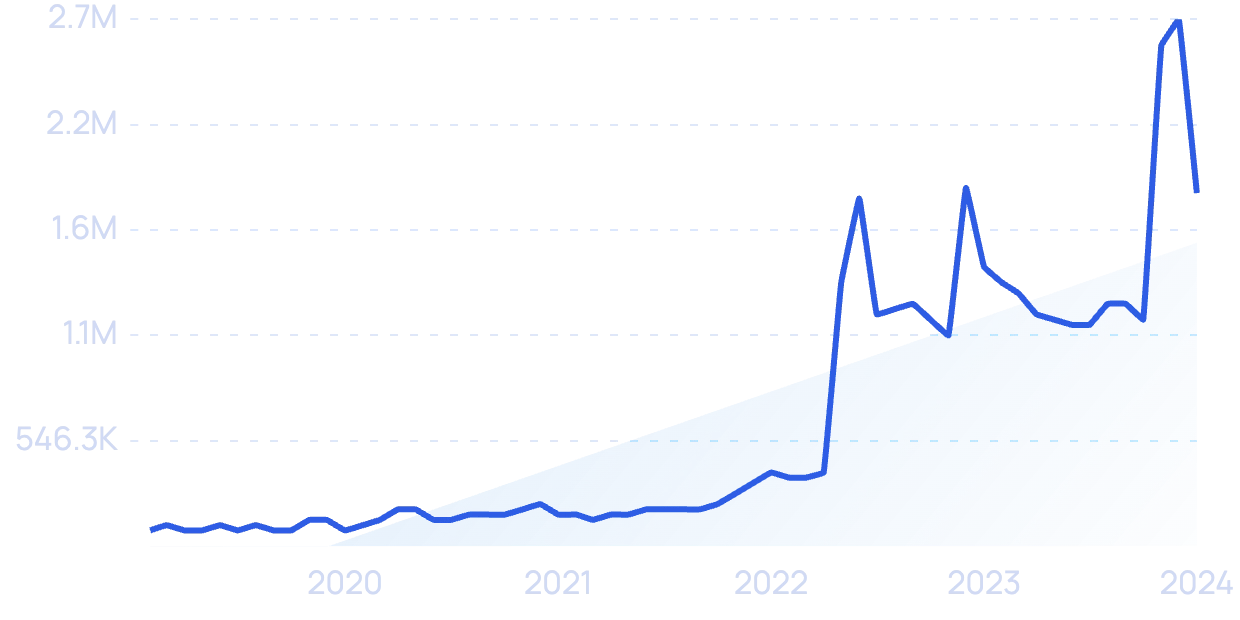
Searches for “cloud gaming” have grown by 1,775% in the last 5 years.
There were approximately 21.7 million paying users who spent roughly $1.5 billion on cloud gaming in 2021.
In 2024, this market’s yearly revenue is forecast to quadruple to $6.3 billion.
The number of paying users is estimated to grow to 58.6 million, illustrating the rapid growth this industry is set to experience.
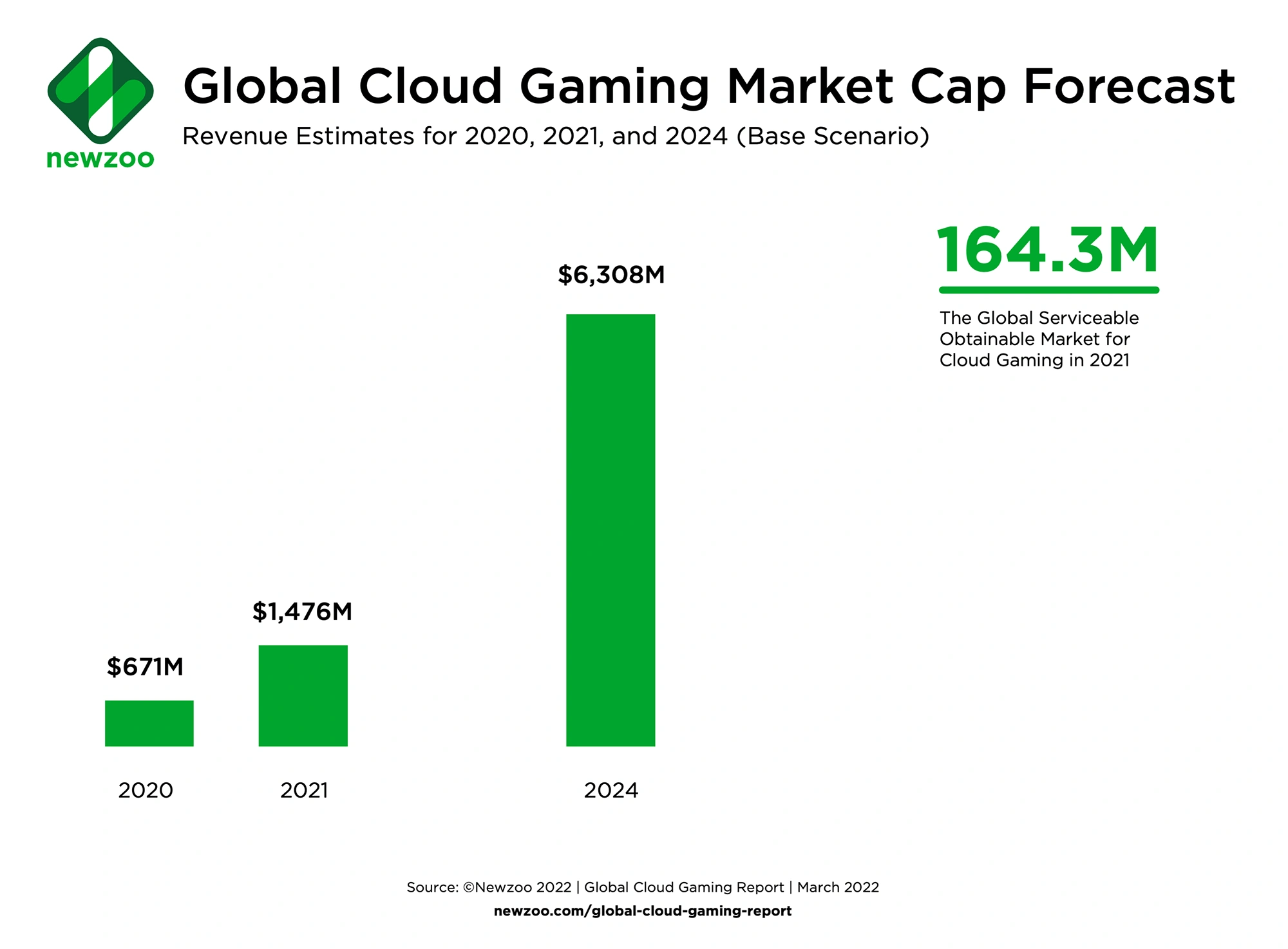
Cloud gaming’s revenue growth in 2024.
So what is behind this growth?
One significant reason is that traditional consoles have become hard to come by.
Chip shortages have significantly impacted console manufacturing. And this shortage has just accelerated people’s dream to game without dedicated hardware.
A growing number of companies are looking to capitalize on this opportunity.
The CES 2022 event saw plenty of companies rolling products/services that support cloud gaming.
Samsung and LG announced support for Google Stadia (Google’s cloud gaming platform) on their smart TVs.
Samsung’s cloud gaming hub.
Finally, cloud gaming is becoming accessible on more devices (smart TVs, TV set-top boxes, and tablets), further accelerating this technology’s adoption rate.
3. Increased Security Concerns
92% of organizations host at least one part of their IT infrastructure in the cloud.
And migration to the cloud is continuing to accelerate.
In fact, 63% of companies will host most (or all) of their IT infrastructure in the cloud in the next 18 months (up from approximately 41% in 2022).
And this dependence on the cloud has given way to a rise in security concerns.
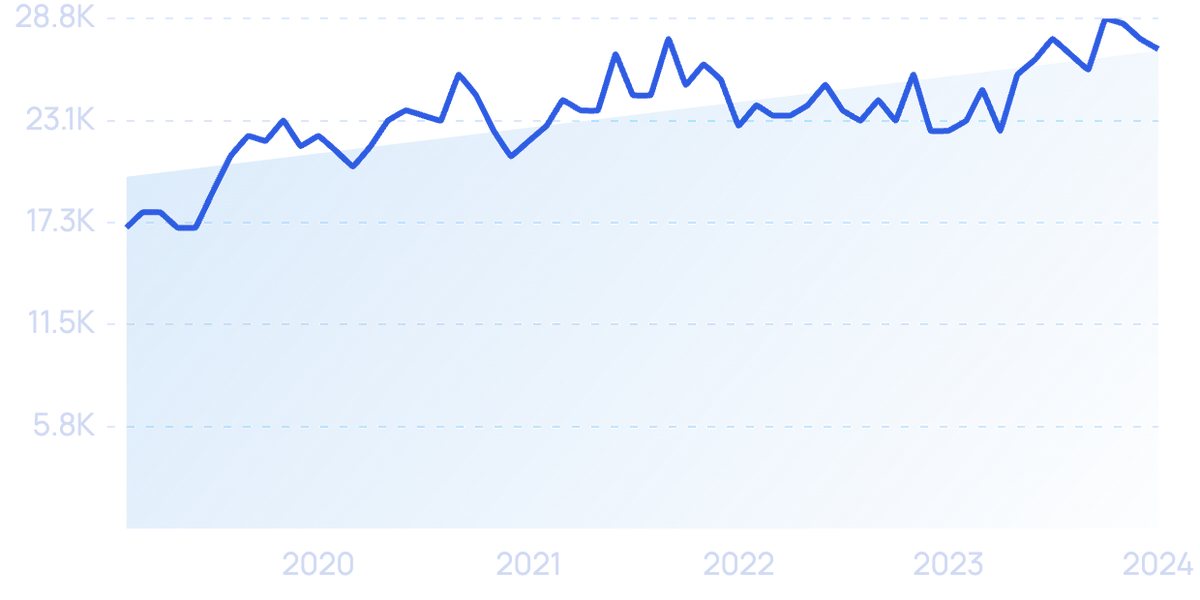
Searches for “cloud computing security” have grown by 59% in the last 5 years.
It is not surprising that security is getting more attention, considering that cloud breaches are becoming more common.
98% of organizations have experienced at least one cloud data breach in the last 18 months.
More alarmingly, 67% reported over three cloud data breaches in the same period.
This is a concerning number, considering that only around 20% of companies dealt with cloud security issues in 2020.
Approximately 69% of companies say that data leakage/loss is the most common cloud security concern.
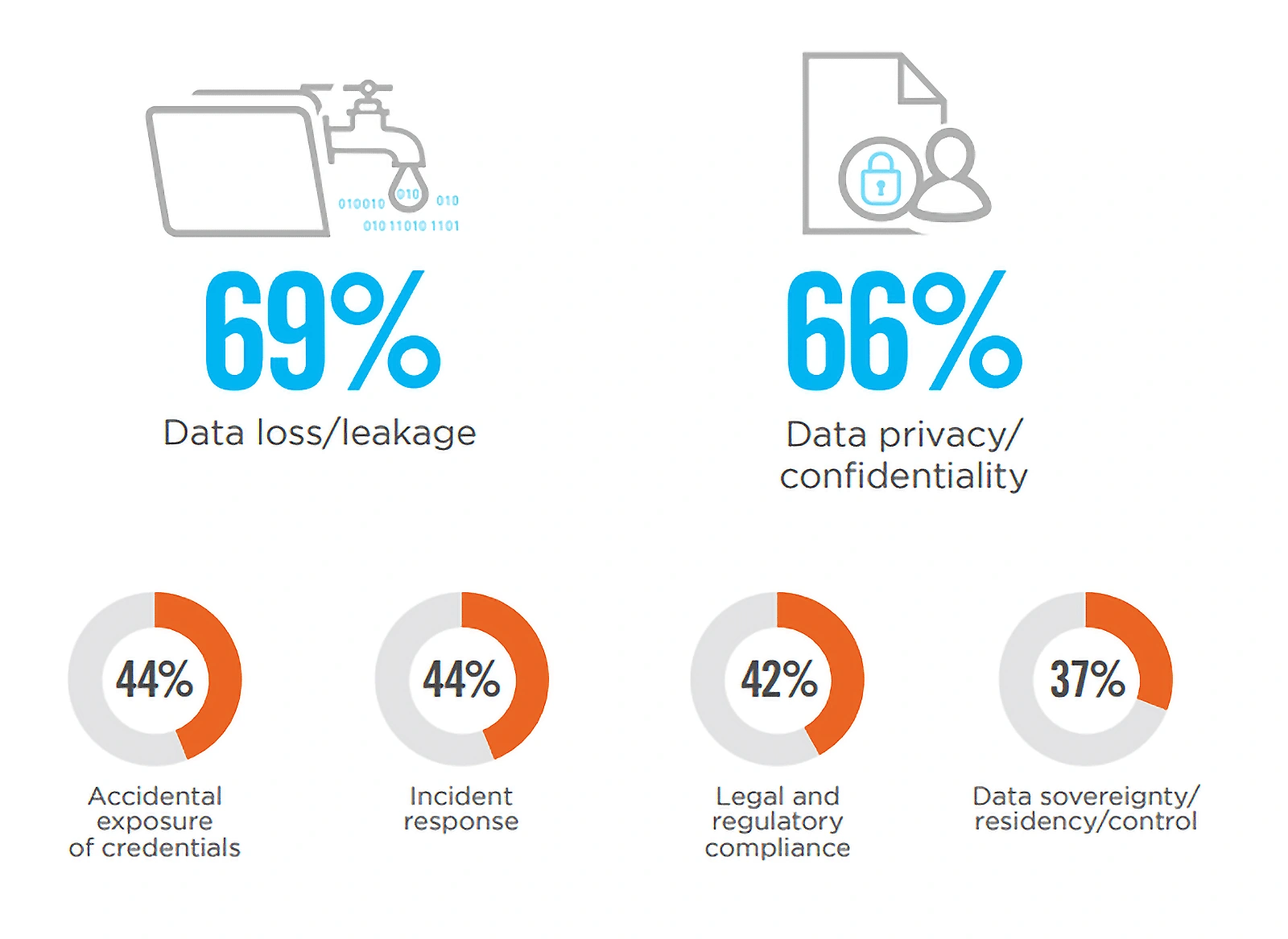
Top cloud breach concerns.
All this is why spending on cloud security was forecast to grow by 33.8% in 2022.
4. Multi And Hybrid Cloud Continues To Grow
Both multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud are infrastructures that utilize more than one cloud system.
So what is the difference between these two approaches?
Multi-cloud refers to an infrastructure that uses multiple clouds that belong to the same system (for instance, companies that use two or more public clouds or two or more private clouds have a multi-cloud strategy).
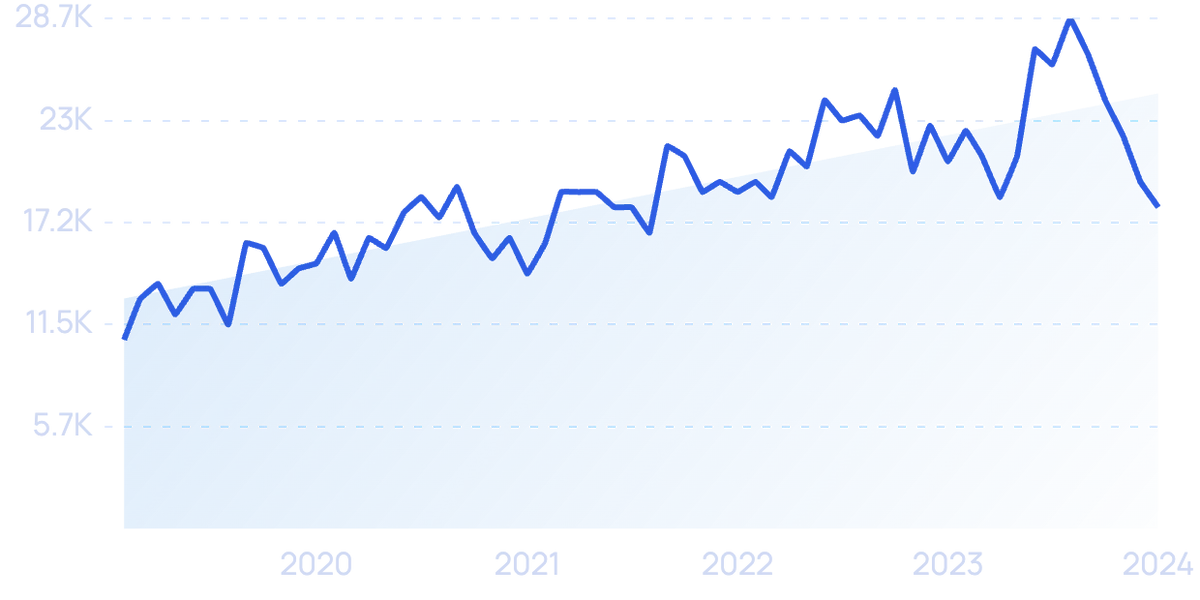
Searches for “multi-cloud” have grown by 70% in the last 5 years.
76% of organizations have adopted a multi-cloud strategy. This number is estimated to grow to 86% in 2024.
The larger the organization, the more likely it adopt a multi-cloud strategy.
94% of large enterprises (>5,000 employees) utilize a multi-cloud infrastructure.
This is mainly because larger firms get better results from this system (64% of large companies say that multi-cloud has been a success).
Hybrid-cloud refers to an infrastructure that blends multiple different types of clouds (for example, companies that use one or more public clouds and one or more private clouds have a hybrid-cloud architecture).
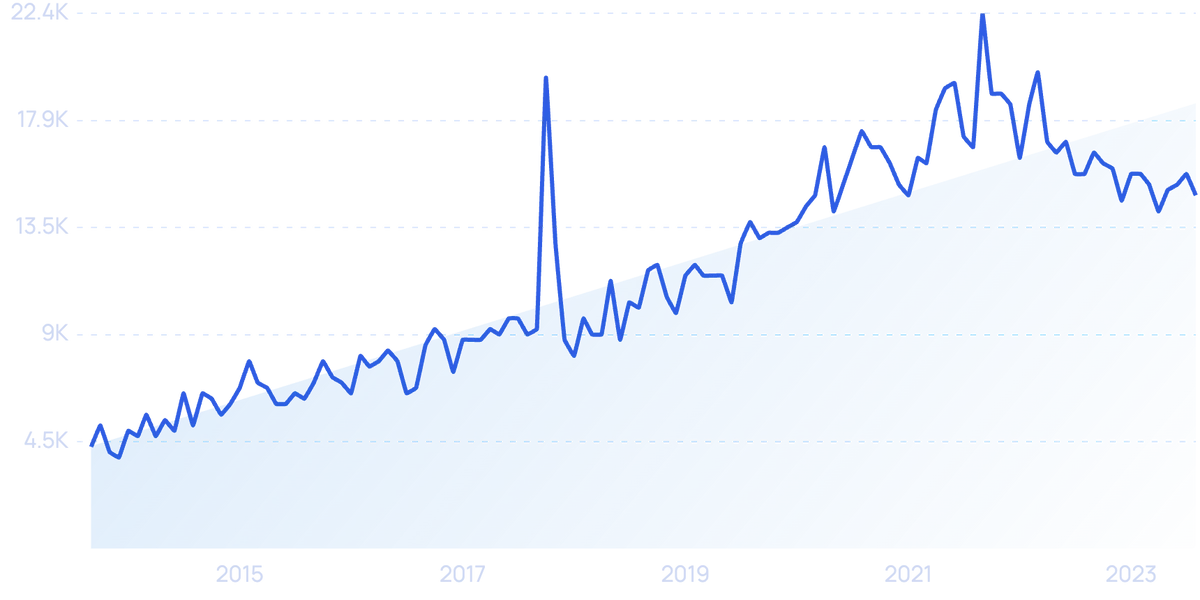
Searches for “hybrid cloud” have grown by 214% in the last 10 years.
A hybrid cloud infrastructure is used by around 80% of organizations (this is up from 58% in 2019), and 43% use multiple public and multiple private clouds.
Improved scalability and control, increased agility, reduced costs, and better support for remote workers are some of the reasons companies implement this approach.
And the adoption of this architecture is expected to continue growing, considering that 66% of IT professionals see hybrid-cloud solutions as a permanent destination for IT infrastructure.
5. AWS Loses Market Share
As of Q4 2021, Amazon Web Services accounted for the largest public cloud market share at 33%.
Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud round up the top three at 21% and 10%, respectively.
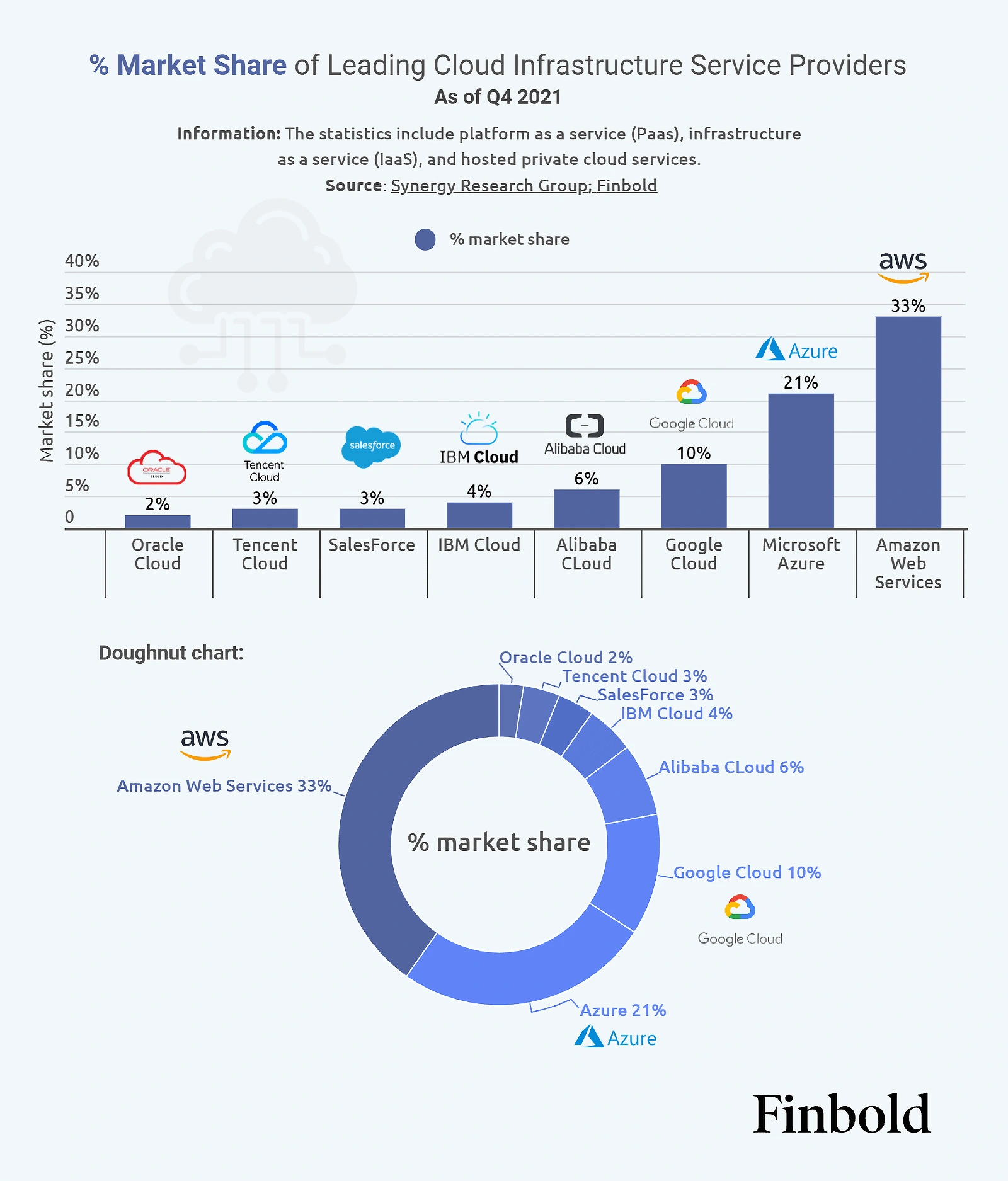
Top eight public cloud providers by market share as of Q4 2021.
In 2019, AWS accounted for 44.6% of the market, and this number fell to 40.8% in 2020.
These figures show that, while still at the top spot, AWS is quickly losing market share in this space.
Furthermore, AWS has already lost the first spot with some specific cloud users.
According to Flexera’s 2022 State of the Cloud report, Azure has surpassed AWS among light and moderate cloud users and is quickly shrinking the gap with heavy users.
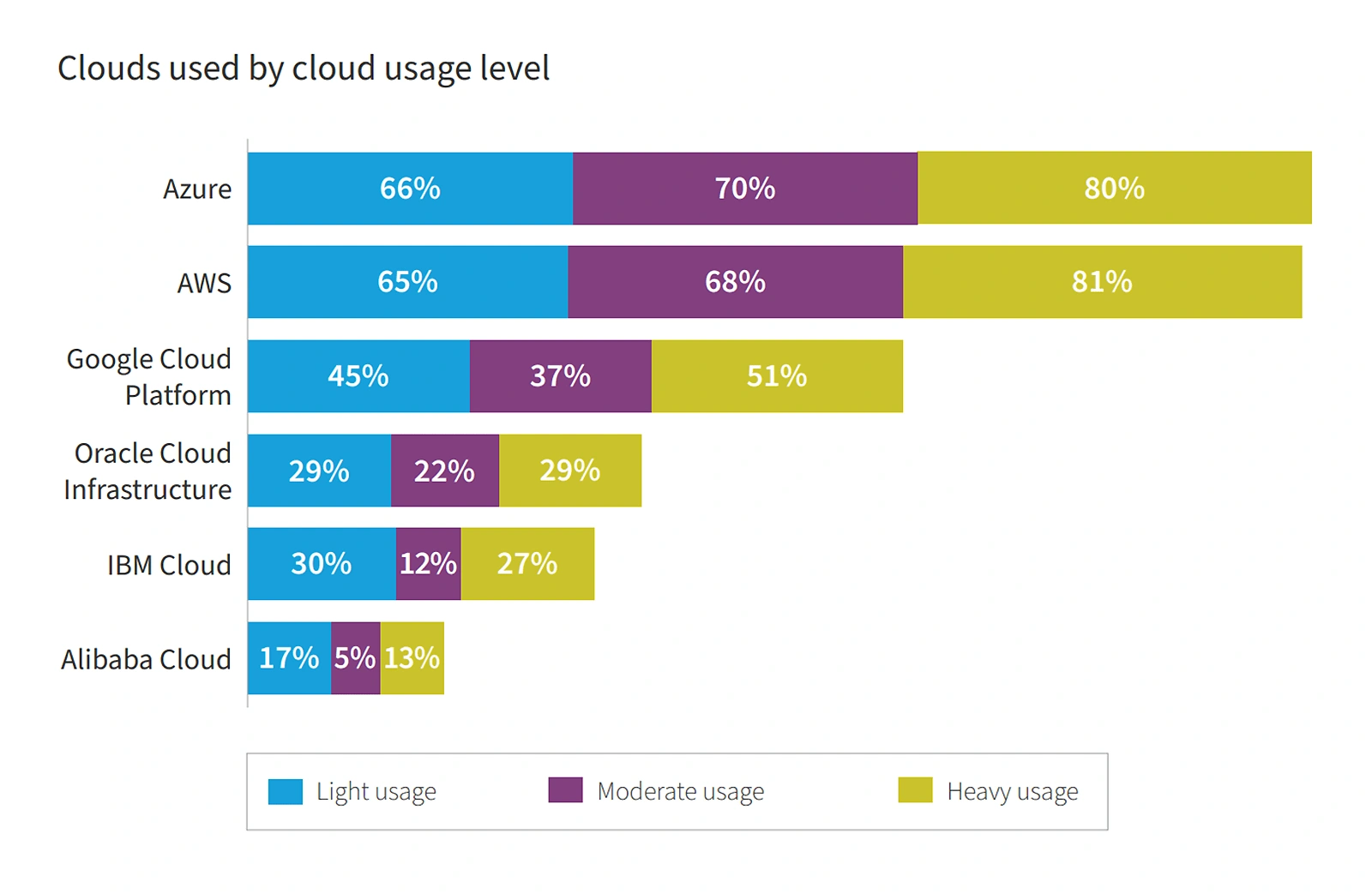
Cloud providers ranked by percentage of cloud usage level.
And for the first time in Flexera’s report’s 11-year history, IT pros said that they preferred Azure to AWS as their public cloud provider in 2021.
Supporting tools are a significant reason behind this trend. More IT professionals preferred using Azure Resource Manager over AWS CloudFormation.
6. Accelerated Spending On The Public Cloud
Public cloud is an IT model where cloud computing services and infrastructure are managed by a third-party organization. These services are shared with other organizations via the public Internet (AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud are some examples of public clouds).
As many as 96% of organizations use the public cloud (80% use it as part of their hybrid cloud infrastructure, 7% only use multiple public clouds, whereas 9% use a single public cloud).
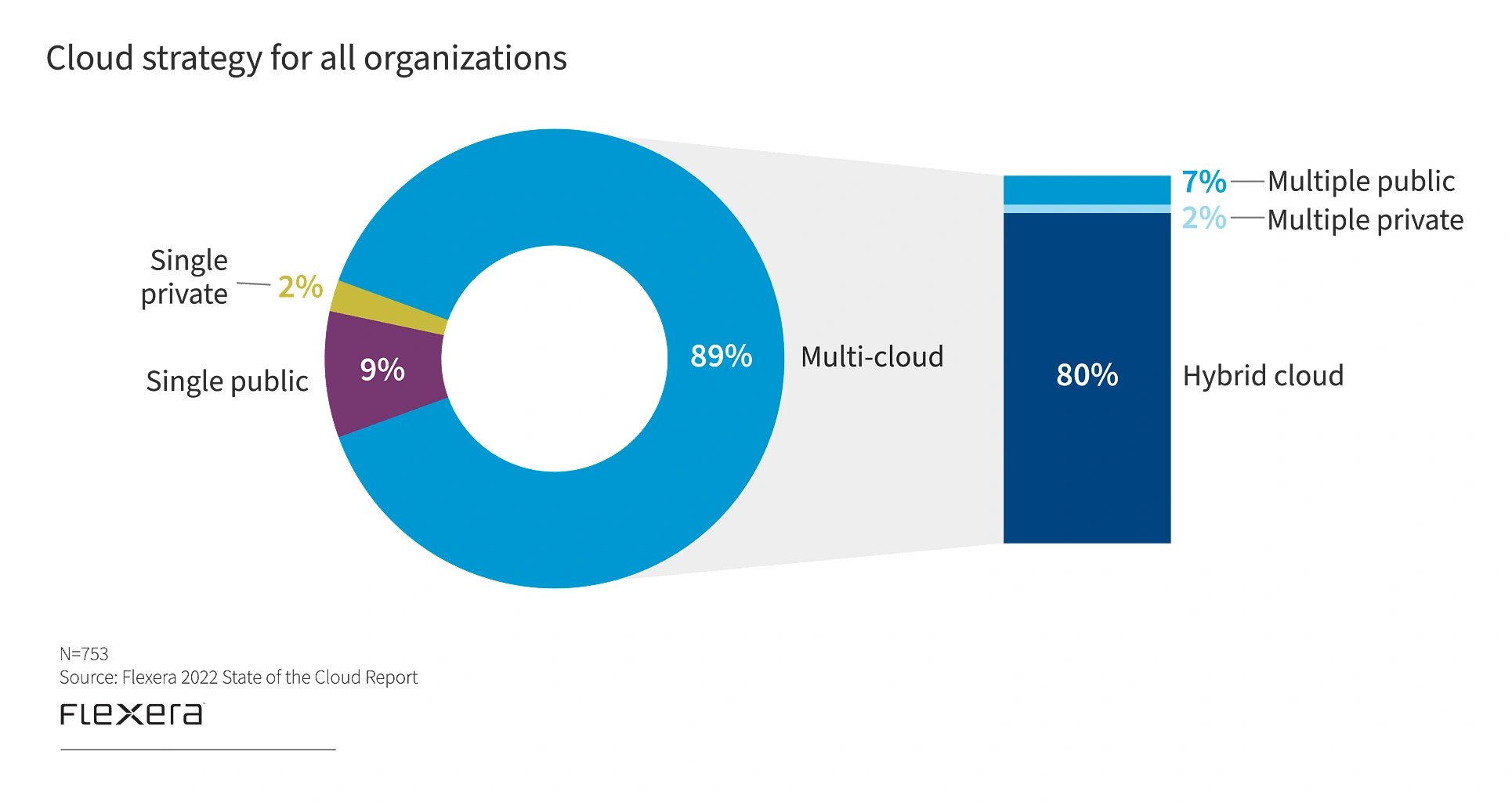
Cloud strategy for all organizations.
While public cloud adoption rates are expected to remain approximately the same for the next couple of years, public cloud usage among these companies is growing.
And this is leading to increased spending on the public cloud.
According to Gartner, public cloud spending was expected to grow 20.4% in 2022, reaching $494.7 billion.
A similar growth rate is forecast for 2024 as well.
This growth, compared to the 17.5% rate in 2019, illustrates that public cloud spending is accelerating.
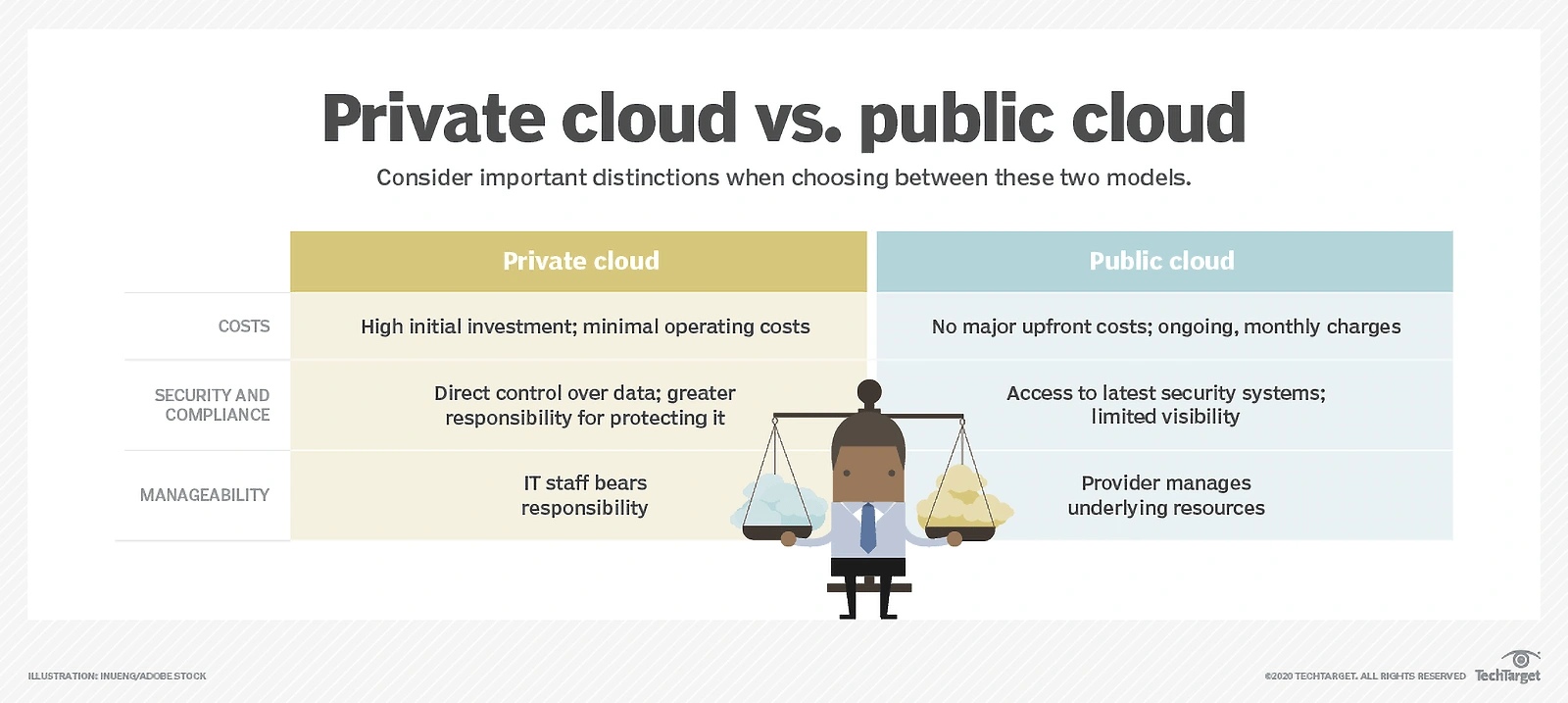
Public and private cloud benefits.
The following are some of the reasons why companies are opting to use the public cloud:
- Lower costs: organizations only pay for what they use (no hardware or software purchases)
- No maintenance: the public cloud provider handles maintenance
- Scalability: on-demand resources can meet any usage needs
- Reliability: a large network of servers ensures security
7. Cost Savings Remain A Top Priority
Approximately 82% of organizations say that implementing cloud systems turned out to be more expensive than initially thought.
They indicated their public cloud spending was over budget by an average of 13%.
Searches for “cloud cost monitoring” have grown by 300% in the last 5 years.
A large part of this cost comes from inefficiencies and mismanagement of cloud infrastructure.
When asked about how efficient their cloud management strategy is, companies responded that approximately 32% of their cloud spend is wasted, up from 30% in 2021.
Idle cloud space and overprovisioning are two of the most significant reasons for cloud waste.
For quantification purposes, around $14.5 billion is wasted on idle cloud resources, whereas $8.5 billion is the estimated amount of cloud waste from over-provisioning.
All this is why companies are trying to find ways to optimize their cloud costs.
Searches for “cloud cost optimization” have grown by 483% in the last 5 years.
Optimizing cloud usage, according to Flexera, was the top cloud initiative for 2022 (the sixth consecutive year this challenge got the top spot).
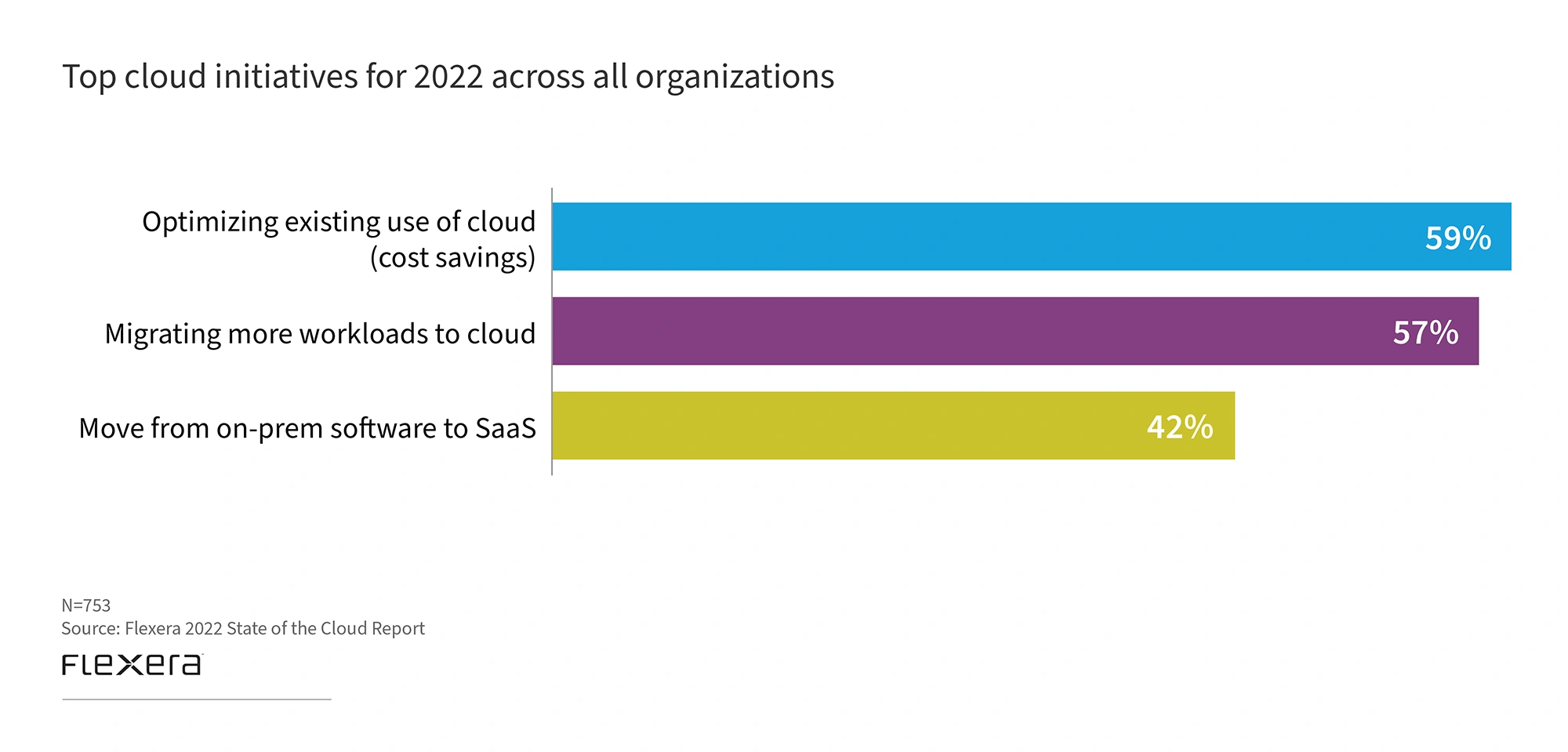
Top three cloud initiatives for 2022.
Conclusion
This completes our list of the seven most crucial cloud computing trends for 2024 and beyond.
From cloud gaming to edge computing, it is a fascinating time to be following what happens in this space.
Finally, it will be exciting to see how companies balance the need to increase cloud usage with the necessity to optimize cloud spending.