Adoption of Artificial Intelligence in healthcare

- Artificial intelligence can help healthcare workers do more with limited resources.
- Artificial Intelligence platforms, increasingly utilised in public health, use complicated data systems as a crucial component for health emergency readiness.
- AI-powered diagnostic solutions in Rwanda and Ghana are enhancing medical imaging analysis, contributing to the early detection of diseases like cancer and tuberculosis.
Artificial intelligence in healthcare is the art of integrating human ability into machines programmed to impersonate human actions. AI’s application in healthcare primarily helps medical practitioners in many aspects of patient care, including administrative procedures.
As of 2020, the application of Artificial intelligence in healthcare in the USA and Canada slashed healthcare expenses by around 25 per cent and 13 per cent, respectively, giving healthcare providers time to give more of their limited resources to patient care issues. AI deep learning procedures have also saved many lives globally by decreasing the diagnosis-treatment-recovery cycle for patients, Africa is no different.
The evolution of AI holds immense potential to automate healthcare systems in Africa by changing medical procedures. AI is quickly changing healthcare in Africa, and the continent needs to equip itself for this inevitable transformation. However, its application in Africa is still in its foundations, particularly on the issues of the global burden of diseases, currently at 25 per cent.
With the advancements in medical procedures, AI can help healthcare workers do more with limited resources. There is much to learn from already thriving nations that are transforming health through AI.
Read Also: Artificial intelligence (AI) could create a turning point for financial inclusion in Africa
Adoption of AI in healthcare in Africa
AI platforms, increasingly utilized in public health, use complicated data systems as a crucial component for health emergency readiness. Yet, Africa faces many challenges in the availability, analysis, and use of data to inform health decision-making. Countries with limited access to their demographic data struggle to use it for program advancements.
Crediting this to the rapid adoption of mobile phone technologies in the region, Africa is poised to use AI algorithms to enhance the adoption, accessibility, and usage of data for healthcare improvement.
In 2021, a virtual workshop was organised to discuss solutions for the responsible development and adoption of AI in Africa. A report thereafter revealed some critical policies in strengthening the digital health environment by high-level policymakers, technical experts, academia, and public and private sector partners.
High-end data privacy, sharing protocols, training and creating platforms for researchers’ funding and healthcare models, developing frameworks for assessing and implementing AI, organising workshops and conferences on AI, and instituting regulations, governance, and ethical guidelines for AI were highlighted as critical measures needed in digitalising healthcare.
For instance, AI-powered diagnostic solutions in Rwanda and Ghana are enhancing medical imaging analysis, contributing to the early detection of diseases like cancer and tuberculosis. Additionally, companies like Zipline are optimizing drone delivery routes for medical supplies through AI, improving access to essential medications in remote areas, and strengthening healthcare systems.
It calls for the need to adopt proper healthcare systems in planning for AI to mitigate inefficiencies and incompetency while increasing effectiveness in the adoption of AI. Thus, firm collaborations and partnerships among governments and stakeholders should be key.
Challenges facing AI in healthcare systems
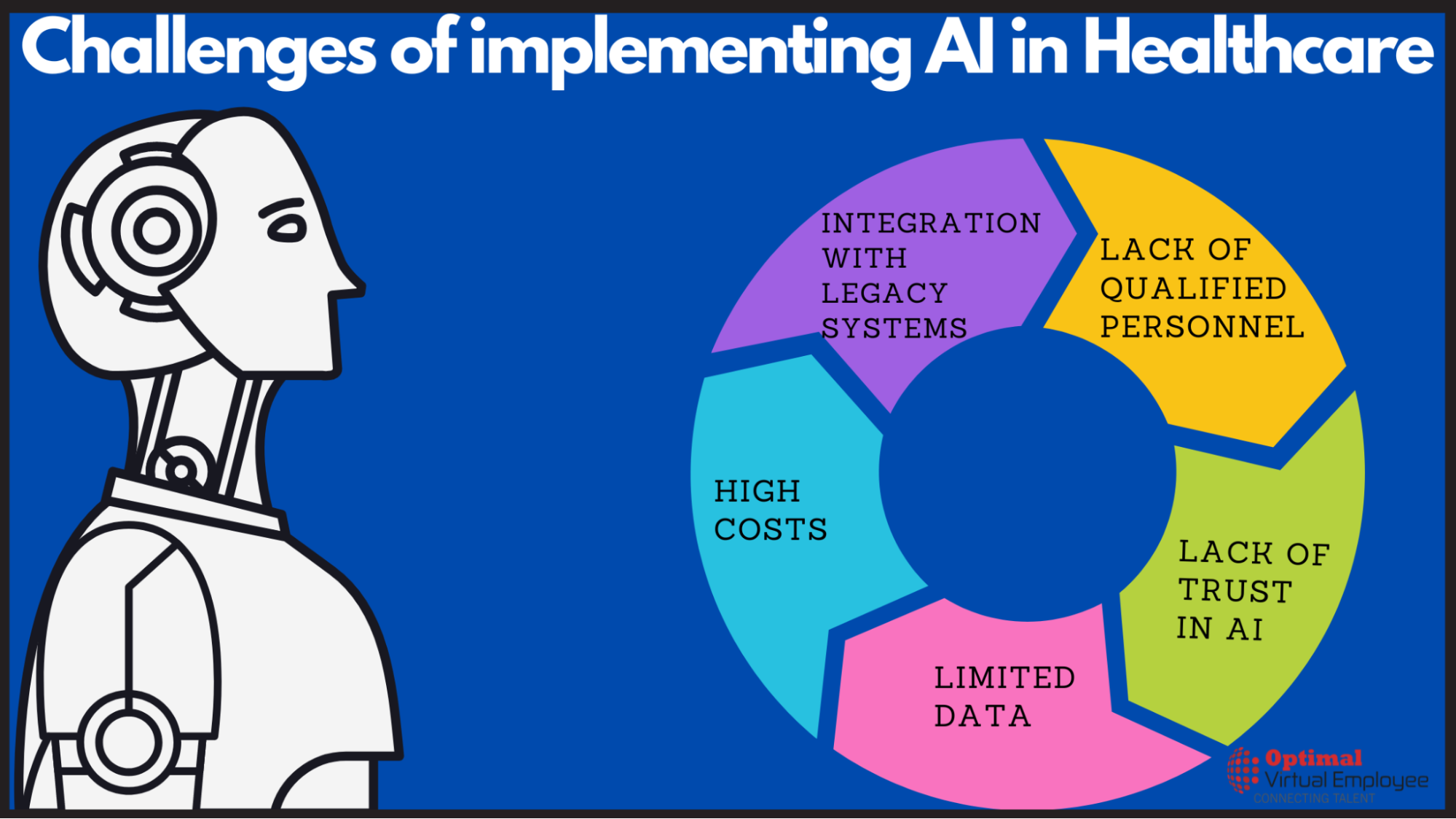
Despite its potential, the adoption and utilization of AI in Africa face several limitations. These challenges include a shortage of relevant technical skills, inadequate infrastructure, limited investment in research and development, and the need for adaptable regulatory frameworks.
The major obstacle is the skills gap, particularly among the youth, which prevents Africa from fully embracing transformative technologies like artificial intelligence in healthcare. Additionally, data limitations hinder the development of AI applications, as there’s a scarcity of high-quality and diverse data reflecting the local context. Limited funding for research and development further impedes progress in artificial intelligence innovation.
There’s also concern about the displacement of jobs due to automation. However, integrating AI into production processes can enhance productivity, improve human capabilities and skills, generate new job roles, and potentially reshape existing ones rather than replace human workers.
Furthermore, cultural skepticism, lack of understanding of AI, and the challenge of integrating AI with existing systems present additional barriers.
Policy frameworks also play a pivotal role, with many countries lacking robust policies and legislation on digitalisation. Nonetheless, efforts by some nations, such as Ethiopia, Ghana, Rwanda, and Mauritius, to formulate AI strategies underscore progress in this arena.
Read Also: Get better, more accurate search results with Chat GPT’s latest update
Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
AI can improve outcomes and decrease the cost of treatment. Through crucial technological advancements, Artificial intelligence in healthcare assures quality diagnostic and medical procedures. It will advance supply-chain efficiencies with fewer administrative responsibilities and modernise life-saving conformity measures.
Artificial intelligence in healthcare can provide a platform where patients can freely ask medical-related questions and receive instant feedback, acquire extra information and reminders concerning taking medications, report information to doctors, and achieve extra medical assistance. Consequently, it promises growth in terms of precision and efficiency, leading to relatively fewer human mistakes and reduced doctor visits.
Conclusively, Artificial intelligence in healthcare is no longer an imaginary promise but an unavoidable reality. It has left research laboratories and become a lifestyle in many developed nations. Due to its potential, partners, and governments around the continent are taking steps and combining forces to ensure responsible development and use of AI. There is still much to be learned from organizations that are changing health outcomes worldwide, and Africa is no exception.
Future Outlook: Opportunities for AI In the Health Sector in Africa
The integration of Artificial intelligence in healthcare in Africa holds meaningful potential across diverse sectors, with significant economic projections and practical applications. From economic growth projections to practical applications in healthcare, agriculture, urban development, and education, there is a concerted effort to harness AI’s potential across various sectors and countries on the continent.
Collaborative initiatives, including partnerships with international tech firms and AI research institutions, are bridging some of these gaps. However, the journey to full-fledged Artificial intelligence in healthcare adoption in African statistical systems remains fraught with challenges.
While enthusiasm for Artificial intelligence in healthcare abounds, Africa must address infrastructural, financial, human resource, and policy hurdles to fully embrace the transformative power of AI in healthcare. With strategic investments and collaborative efforts, Africa can navigate these challenges and lead in innovative AI applications for societal progress and economic development.