Israeli startup unveils AI robot capable of house chore

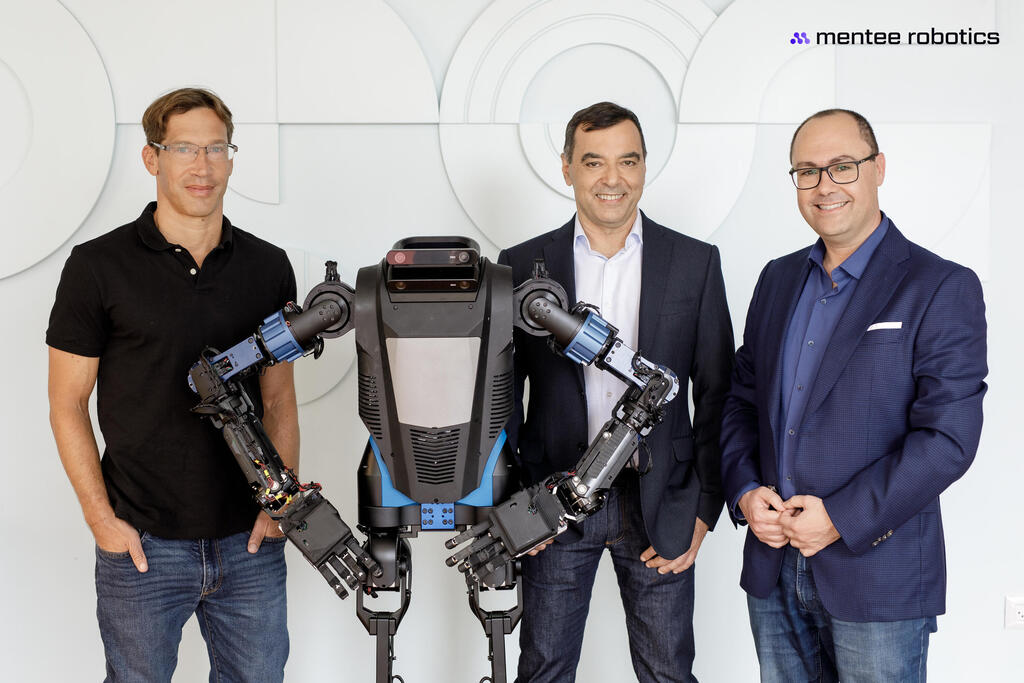
Professor Amnon Shashua, who previously co-founded Mobileye, has announced the launch of a new humanoid robot enhanced with artificial intelligence, in collaboration with his colleagues, Professor Shai Shalev-Shwartz and Professor Lior Wolf. This innovative robot is expected to hit the market in the first quarter of 2025. While the company has yet to reveal its price, it is anticipated to be affordable, targeting both corporate and domestic environments.
Humanoid robots are not a novelty in industrial and home settings, but integrating them with advanced artificial intelligence represents a significant breakthrough. Among the firms working on similar technologies are Elon Musk’s Tesla with its Optimus project launched roughly three years ago, Xiaomi with CyberOne introduced about two years ago, and Boston Dynamics with its Atlas robot, which debuted in 2013 and was recently decommissioned. Alongside global giants like Dyson, Honda, and Huawei, several Israeli startups, including Unlimited Robotics, are also venturing into the development of humanoid robots. Nevertheless, Mentee Robotics claims their model is the first to incorporate AI technology comparable to that found in OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google’s Gemini, or Anthropic’s Claude.
The primary benefit of employing AI akin to ChatGPT is the robot’s proficiency in processing and executing commands in straightforward human language. Mentee Robotics states that their robot can manage an entire operational cycle autonomously. This cycle starts with a verbal command and encompasses complex functions such as navigation, movement, contextual awareness, object identification and positioning, grasping, and natural language comprehension. The robot’s operations are powered exclusively through camera-based sensors and proprietary electric motors that provide remarkable agility and seamless integration of artificial intelligence.
Founded in 2022 by Professor Amnon Shashua, who is the chairman, along with Professor Lior Wolf as the CEO, and Professor Shai Shalev-Shwartz, Mentee Robotics has been quietly developing a humanoid robot designed for a broad array of tasks in both private residences and industrial warehouses. The company named its prototype the Menteebot, which features artificial intelligence integrated into every level of its operation. The robot’s movement technology employs a cutting-edge machine learning method known as simulation to reality (Sim2Real). This method involves training in a simulated environment that replicates the robot, utilizing a vast pool of data. This allows for the adaptation to the real world using significantly less data, maintaining the system’s efficiency.
Using NeRF-based algorithms, which are part of the latest advancements in neural networks for three-dimensional scene representation, the robot performs environmental mapping in real time. These 3D models, enriched with semantic information, generate cognitive maps that enable the robot to instantly query and identify objects and locations. According to the company, the robot can pinpoint its position on the 3D map and autonomously devise dynamic paths while dodging obstacles.
For interpreting commands and building the necessary steps to execute a task, large language models based on transformers (LLMs) are employed. The robot’s design emphasizes the coordination between its leg and arm movements, allowing for dynamic balancing during tasks like carrying weights or reaching.
The prototype unveiled today, though not the final iteration of the robot, showcases an end-to-end functionality for the first time—from receiving a verbal command to completing a complex task involving navigation, movement, environment comprehension, object detection and positioning, grasping, and understanding natural language.
Professor Shashua remarked, “We are on the brink of a convergence of multiple technologies—computer vision, natural language understanding, sophisticated simulators, and methods for shifting from simulation to reality.” He views this integration as foundational for the future design of humanoid robots that can seamlessly navigate human environments and perform tasks with advanced perceptual capabilities.