Riding the Wayve of AV 2.0, Driven by Generative AI
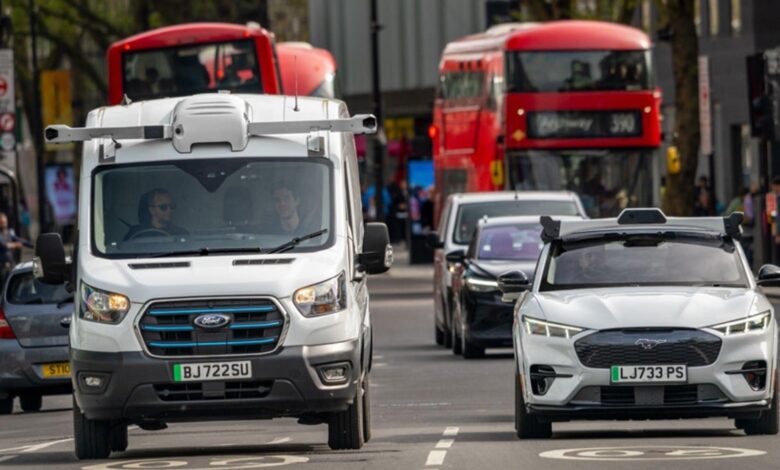

Generative AI is propelling AV 2.0, a new era in autonomous vehicle technology characterized by large, unified, end-to-end AI models capable of managing various aspects of the vehicle stack, including perception, planning and control.
London-based startup Wayve is pioneering this new era, developing autonomous driving technologies that can be built on NVIDIA DRIVE Orin and its successor NVIDIA DRIVE Thor, which uses the NVIDIA Blackwell GPU architecture designed for transformer, large language model (LLM) and generative AI workloads.
In contrast to AV 1.0’s focus on refining a vehicle’s perception capabilities using multiple deep neural networks, AV 2.0 calls for comprehensive in-vehicle intelligence to drive decision-making in dynamic, real-world environments.
Wayve, a member of the NVIDIA Inception program for cutting-edge startups, specializes in developing AI foundation models for autonomous driving, equipping vehicles with a “robot brain” that can learn from and interact with their surroundings.
“NVIDIA has been the oxygen of everything that allows us to train AI,” said Alex Kendall, cofounder and CEO of Wayve. “We train on NVIDIA GPUs, and the software ecosystem NVIDIA provides allows us to iterate quickly — this is what enables us to build billion-parameter models trained on petabytes of data.”
Generative AI also plays a key role in Wayve’s development process, enabling synthetic data generation so AV makers can use a model’s previous experiences to create and simulate novel driving scenarios.
The company is building embodied AI, a set of technologies that integrate advanced AI into vehicles and robots to transform how they respond to and learn from human behavior, enhancing safety.
Wayve recently announced its Series C investment round — with participation from NVIDIA — that will support the development and launch of the first embodied AI products for production vehicles. As Wayve’s core AI model advances, these products will enable manufacturers to efficiently upgrade cars to higher levels of driving automation, from L2+ assisted driving to L4 automated driving.
As part of its embodied AI development, Wayve launched GAIA-1, a generative AI model for autonomy that creates realistic driving videos using video, text and action inputs. It also launched LINGO-2, a driving model that links vision, language and action inputs to explain and determine driving behavior.
“One of the neat things about generative AI is that it allows you to combine different modes of data seamlessly,” Kendall said. “You can bring in the knowledge of all the texts, the general purpose reasoning and capabilities that we get from LLMs and apply that reasoning to driving — this is one of the more promising approaches that we know of to be able to get to true generalized autonomy and eventually L5 capabilities on the road.”