Types, Use Cases, and Implementation

In a matter of two years, by 2026, the IoT market will reach $650.5 billion. However, there are very few people who know the technology’s mechanics – how it collects, processes, and shares data.
Here’s a quick explanation for you.
A majority of the IoT systems ingest data via a streaming platform, which is then cleaned of noise and set up for analytics. Usually, an IoT app uses real-time analytics which can execute aggregations on a high volume of fast-moving data. The outcome is either visualized for end users or get exported via API to some other application for further action by IoT data analytics.
Now while IoT systems and their use cases can vary greatly on the basis of applications and designs, the data sets which the technology measures can be divided into three prime categories –
- Status data: It is a basic, raw set of data which communicates the device or system status.
- Automation data: This data type is built by automated devices and solutions like automated lighting and smart thermostats.
- Location data: The data communicates the geographical location of a device or solution. The most common use case of it can be found in warehousing, logistics, and manufacturing.
While seemingly straightforward, what IoT analytics solutions do is far from easy.
Some Roadblocks in the Way of IoT Data Analytics
Operating in both digital and physical worlds, IoT systems present unique challenges for implementation and analysis. The top one being data privacy and security, especially when privacy regulators like EU’s GDPR and California Consumer Privacy Act levy high penalties for violations. Scared of a negative outcome, several IoT companies are reluctant about moving to the cloud, leaving them with fully on-premise or hybrid environments.
Another challenge is that data can be diverse, which in turn can be difficult to process or analyze. What makes it worse is that different IoT devices work on different firmwares and transmit multiple data formats, making it complex for IoT data management and analytics platforms to categorize and process data.
Lastly, IoT app development and analysis call for unique skills ranging from cybersecurity, data security to expertise around physical hardware maintenance.
To solve some of these evident challenges that businesses face with IoT analytics application on a widespread scale, several IoT analytics platforms have come into existence.
What Does IoT Analytics Solutions Do?
An IoT data management and analytics software is responsible for processing, storing, and analyzing datasets that come in from multiple internet-connected devices in order to get insights, find patterns, and make data-backed decisions.
Modern-day IoT analytics services tend to utilize next-gen data analytics technologies like deep learning, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, to study data coming in from multiple sources.
The features list of a typical IoT analytics application can include –
- Data collection
- Data storage
- Data processing
- Data visualization
- Generation of actionable insights
Types of IoT Data Analytics Platforms
One of the first questions that IoT entrepreneurs have when it comes to looking for the best solution for their operations is which kind of IoT analytics solutions to introduce in the system. Here’s an overview of the types which also help cement the IoT analytics use cases.
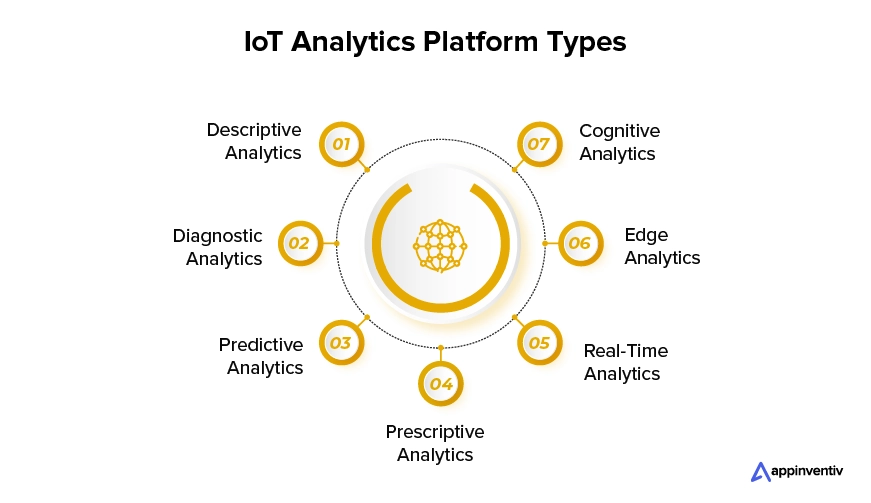
Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive IoT analytics utilizes historical data analysis to summarize past events, enabling organizations to understand previous occurrences and discern trends and patterns that may inform future decisions. This type of analysis generates detailed reports about what happened, when it happened, and the frequency of occurrences after processing and analyzing data from IoT devices.
Such insights help identify any irregularities and provide valuable answers to questions about the behavior of objects or people, guiding strategic planning and operational improvements.
Diagnostic Analytics
Diagnostic IoT analytics delves deeper than descriptive analytics by addressing why certain events occur, identifying the root causes of problems through a detailed examination of data. It leverages methodologies such as data mining and statistical analysis to uncover hidden patterns and relationships within the data.
This form of analytics provides actionable insights, helping to understand the origins and implications of specific issues, enabling more informed decision-making and problem-solving strategies.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics utilizes historical data and various statistical and machine learning algorithms to model and forecast future events, aiding in business decisions such as inventory and demand forecasting. This technology is pivotal in predictive maintenance, where it employs analytics and alerts to detect early signs of equipment wear and tear, especially in sectors like healthcare, automotive, and aerospace.
This approach reduces the need for physical inspections, minimizes downtime, and accelerates response to anomalies by continuously comparing sensor data against established operational algorithms, thus enhancing overall operational efficiency and preventative care.
Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive IoT analytics represents the pinnacle of IoT data analysis by not only forecasting future events but also providing actionable guidance on the optimal steps to achieve business goals. This sophisticated form of analytics integrates the insights from descriptive, diagnostic, and predictive analytics to recommend actions that optimize operations. It uses optimization algorithms to determine the best courses of action.
Moreover, by amalgamating the company’s own data—such as technical specifications, manuals, and past Q&As—with IoT data analytics, the system not only identifies issues in real-time but also leverages historical data to suggest proven solutions, facilitating quick, accurate responses and enhancing predictive maintenance efforts. This holistic approach significantly boosts the efficiency of technical support and operational decision-making.
Real-Time Analytics
Real-time Internet of Things data analytics enables the immediate processing, analysis, and interpretation of data from IoT devices to deliver actionable insights and facilitate informed decision-making. By utilizing advanced analytical tools, including machine learning algorithms and statistical models, this approach identifies patterns, trends, and anomalies in the data, thus optimizing operations across various fields.
For instance, in manufacturing, real-time analytics monitor and refine production processes, while in healthcare, they assess patient health and flag potential issues early on. This capability helps organizations improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance overall effectiveness.
Edge Analytics
Edge analytics processes data at its source on the network’s edge, significantly reducing latency and improving response times by eliminating the need to send data to central servers. This technology, particularly crucial for IoT applications with large data needs like industrial IoT and automotive systems, enhances data processing speeds and reduces the load on cloud servers.
With the advent of 5G and higher data transfer rates, edge analytics enables IoT devices to perform essential data processing and decision-making locally, though some scenarios still combine edge and cloud computing to manage data more effectively.
Cognitive Analytics
Cognitive IoT data analytics leverages cognitive computing and AI to analyze extensive data from IoT devices, facilitating smarter decision-making and automation by revealing patterns and insights. This approach employs machine learning, natural language processing, and other sophisticated analytics to pinpoint trends, anomalies, and predictive insights, thus optimizing operations, enhancing customer experiences, and driving innovation.
Additionally, it improves the maintenance and security of IoT devices by enabling real-time threat detection and reducing downtime and manual intervention, paving the way for more proactive and predictive management.
Technical and Business-Side Benefits of IoT Analytics
The growing network of IoT devices is demanding new levels of connectivity, automation, and intelligence from IoT analytics platforms, along with the assurance that business owners would be able to make the most of the data sets when it comes to strengthening the business decisions. A promise that has brought Internet of Things analytics on the tech map.
Delving into the assurances further, let us look into the business and technical benefits of IoT analytics solutions.
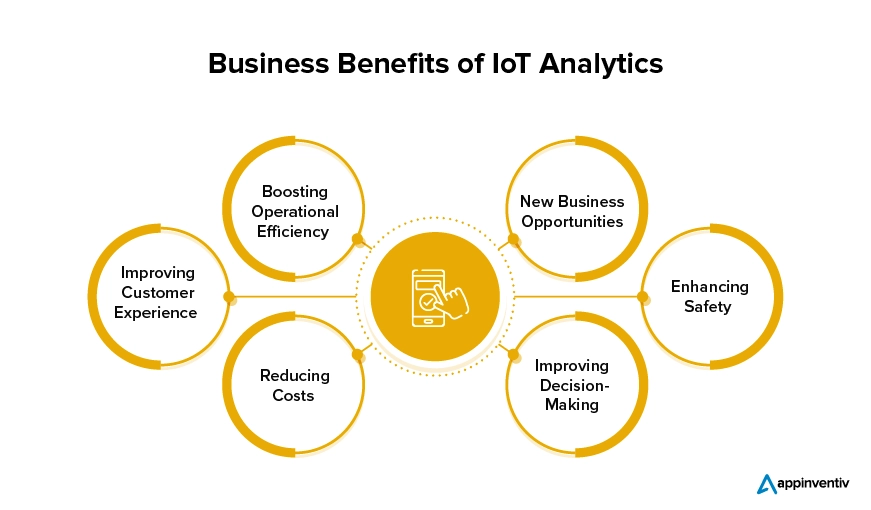
Boosting Operational Efficiency
IoT data analytics allows businesses to rapidly identify inefficiencies by scrutinizing IoT-generated data. For example, a logistics company can implement IoT sensors to monitor fleet performance in real-time, addressing issues like route inefficiencies or vehicle idling times promptly. This immediate insight helps optimize operations and improve fuel efficiency.
Reducing Costs
Leveraging an IoT data analytics solution can significantly reduce costs by improving operational efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and bettering asset management. For example, a manufacturing plant can use IoT sensors to monitor machine health, predicting failures before they occur. This preemptive approach minimizes downtime and extends the life of the equipment, ultimately reducing repair and replacement costs.
Improving Customer Experience
Internet of things data analytics enhances customer interactions by providing detailed insights into consumer behaviors and preferences. For instance, a smart home device company can analyze usage patterns to provide customers with customized energy-saving recommendations, enhancing user satisfaction and engagement with personalized tips that cater to individual usage habits.
Enhancing Safety
Using the system can enhance safety protocols by identifying potential risks early on. In the healthcare sector, hospitals can use IoT devices to monitor critical equipment and patient vitals continuously, quickly detecting anomalies that could lead to health risks, thus allowing for immediate intervention and significantly improving patient safety.
Improving Decision-Making
IoT analytics enhances decision-making capabilities by offering deep insights into operations and customer behavior. For instance, a retail chain can use IoT sensors to track customer foot traffic and purchasing behaviors in real time. This data helps them adjust staffing levels, optimize store layouts, and tailor promotions to increase sales efficiency and customer satisfaction.
New Business Opportunities
It opens up new avenues for business innovation by identifying patterns and trends in consumer behavior. A smart appliance manufacturer, for example, might analyze usage data to identify a demand for energy-efficient features. This insight could lead to the development of a new line of eco-friendly products, tapping into the growing market of environmentally conscious consumers and differentiating the brand in a competitive market.
Real-time Data Analysis
Internet of Things analytics facilitates immediate analysis of data as it’s generated, thanks to streaming analytics technologies. For example, a utility company can use this capability to monitor electrical loads in real-time, adjusting grid operations instantaneously to prevent outages and optimize energy distribution based on current demand, significantly improving operational responsiveness.
Improved Scalability
The systems allow businesses to scale their operations flexibly and cost-effectively. You only pay for the resources you use, which can be dynamically adjusted to meet demand without incurring unnecessary costs. For instance, a cloud-based IoT platform can enable an eCommerce retailer to scale up its inventory tracking during peak seasons and scale down in slower periods, ensuring efficient use of resources.
Increased Accuracy
With IoT analytics, businesses benefit from a high level of precision in their data analysis due to advanced analytical techniques. A healthcare provider could use IoT devices to collect a wide range of patient data continuously, allowing for more accurate and personalized treatment plans based on real-time health status monitoring.
Enhanced Security
Analytics system helps improve security by identifying potential threats before they become significant issues. For example, a financial institution could deploy IoT sensors to monitor its data centers and network traffic for unusual activity, enabling preemptive security measures to thwart cyber threats.
Automation
IoT analytics also supports the automation of processes that traditionally require manual input, reducing labor costs and shifting employee focus to higher-value tasks. For example, a manufacturing plant might implement IoT sensors and automation software to manage the entire production line, ensuring precise material handling, maintenance, and quality control without constant human supervision. This automation not only reduces the likelihood of errors but also enhances the overall efficiency and productivity of operations.
The benefits of applying data analytics for IoT can be best understood by looking into the real-world applications of the software across multiple industries. Let’s get into it.
Real-world IoT Analytics Use Cases
Without us even realizing, IoT is becoming a part of our lives, both directly and indirectly. The driving forces behind this widespread adoption are IoT analytics, which is making it possible for the intelligent solutions to gather, process, store, and create business-impacting insights.
Queue Management Systems
Internet of Things sensors help detect and analyze real-time customer movement in queue management systems. They collect data concerning the movement of customers, time they enter and leave a specific area, and length of queues itself. This data is then studied by IoT analytics to unveil patterns that can later be used to predict peak times, hence allowing businesses to cut staff turnover as well as waiting time. For example, if a queue at the supermarket grows longer, this equipment can be used to open new checkout points improving the level of customer satisfaction.
Example: A number of data points such as customer arrival rate and checkout timing are monitored across all Walmart stores using IoT analytics for effective queue management. This contributes to an efficient operational management system in terms of customer service capacity since staff deployment and availability of checkouts depend on the real-time data insights.
Seamless Shopping Experiences
The beauty of IoT-powered just-walk-out technology is the elimination of old style checkouts. Working in tandem with AI, IoT sensors trail products that shoppers pick using RFID tags information, weight sensors placed alongside shelves or even computer vision technology. The mechanics that work on the backend require the data to be analyzed through IoT analytics prior to accurate store billing through the mobile app, so that the clients automatically pay when they exit.
Example: Amazon Go stores are fitted with IoT sensors and computer vision technology for monitoring shopper activities. In real time it helps in tracking what items are taken from the shelves and updating the virtual cart for frictionless checkout-free shopping.
Intelligent Water Resource Management
The usage pattern analysis and detection of leakage, in real time, are the key of Smart Water Management systems which are equipped with IoT sensors. They gather information about water flow rates; pressure levels as well as other important indications primarily on consumption patterns.
Consequently, utilizing IoT analytics to detect anomalies within this information set up early alarms against potential leaks. In addition, it gives insights on how best water can be utilized without wasting much therefore saving operation cost.
Example: Barcelona integrates the use of IoT into its water management systems for purposes of checking and possibly curbing overuse of water. The analytics software analyzes information from different sensor points to detect leaks, optimize water distribution, and enhance general water conservation in the city.
Agriculture Optimization Tools
The other area where IoT analytics is widely used involves soil analysis and climate data for agronomic purposes. Sensors can collect information about soil moisture levels, temperature rates as well as ph balance in soil samples taken from different parts of your fields at certain times during the day.
Against this backdrop, the information is subjected to IoT data analytics so that farmers can get planting recommendations that lead to higher yields through informed decisions on sustainable land use practices.
Example: Devices hooked onto agricultural machines like John Deere tractors collect information on soil condition. This info is fed into an analytics system that assists farmers with decisions about what types of crops should be grown where they’re located.
Optimized Energy Utilization
The management and control of energy consumption becomes easier through IoT devices. Smart grids collect real-time energy data from power usage, supply and demand through IoT sensors. The information is then passed through an IoT analytics platform that then strategically plans adaptive energy distribution, which leads to substantial cost reduction and also paves the way for less harmful emissions into the environment.
Example: To manage energy use in a sustainable manner, Copenhagen has already employed smart grids. Utilizing data from the many internet-connected devices, the analytics system is able to optimize energy distribution based on requirements for power including renewable sources and administrative issues in general.
Smart Traffic Systems
Integrated traffic signals and street signs run on real-time traffic data they get from the IoT devices installed at the traffic lights and street signs. The movement of cars, congestion levels alongside other forms of data are collected by IoT sensors placed on various roadways, which when analyzed by an analytics-powered energy management system, helps in adjusting traffic signals and helping in urban energy efficiency through reducing the traffic jam.
Example: Singapore uses IoT as part of its traffic management system to enhance mobility.The system’s analytics takes in live stream information on all car movements and pedestrian activities to then adjust the traffic lights’ cycle time at specific intersections where congestion tends to occur most
Remote Health Monitoring
IoT devices are used in healthcare to enable continuous monitoring of patient’s health conditions away from traditional medical environments. They are able to collect vital signs, physical activity data and other functions of the body which can be described as parameters required by any health professional who wants to know how a particular individual is feeling without necessarily having an immediate one on one interaction with them on a daily basis.
To enable this, the collected information needs processing through IoT data analytics so that it provides insights in real-time and facilitates timely intervention in addition to personalized care plans.
Example: Philips offers devices used for healthcare purposes remotely. These devices can sense body temperatures or be used in cardiac monitoring.
Data-Driven Medical Research
IoT applications have been instrumental in gathering large volumes of health data from different sources such as wearables and monitoring devices for purposes of conducting medical research. This level of extensive data gathering makes it pivotal to involve IoT analytics in order to analyze the longitudinal health data that can be adopted in various medical disciplines especially in improving medical research.
Example: The use of IoT as a research tool has resulted in a large amount of easily obtainable data in the medical sector. It allows high-quality investigations through wearables and other devices related to tracking patients’ health trends
Industrial Automation
Precise monitoring of facilities that majorly work with industrial machines is something which is being made possible through IoT technology. By using analytics software to study the data collected from equipments’ functioning, such as – operational states, performance of machines, and their conditions – real-time correction actions can be planned to improve efficiency and reduce downtime during preventive maintenance.
Example: Tesla uses advanced IoT and automation in its factories. The analytics systems they use are believed to process data from IoT sensors to monitor machinery, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production processes, ultimately enhancing manufacturing efficiency and product quality.
Enhanced Building Management
IoT smart building solutions have already created a name in the digital space for improving the efficiency of buildings and occupants’ comfort. This becomes possible through the usage of IoT sensors that collect data around lighting, temperature control, energy consumption, and occupancy status.
The role of an analytics solution here is to automatically process the data and adjust building’s systems like lights or HVAC, based on either energy utilization or comfortable living conditions.
Example: The Edge, in Amsterdam, is known as one of the smartest buildings in the world, utilizes IoT for efficient management of its resources.
Following the same level of success in your industry is going to be highly dependent on two elements – your tech partners and how well you implement the solution in your organization.
The tech partner element can be addressed by partnering with us. At Appinventiv, we have extensive experience in working with connected solutions specifically in line with creating an entire ecosystem of data and devices transmission.
Besides ecosystem development, we have also built a series of smart IoT analytics solutions that have been making it easy for retail houses, healthcare firms, hotels, and service companies to manage their operations better and make informed decisions.
Let’s talk about the second element now – implementation of IoT analytics in your organization.
The process that we typically follow and suggest to our clients looks something like this.
IoT Analytics Implementation Process
Goal Defining
The first step towards IoT analytics implementation is understanding your core business objective. This would include finding the problem, scope of improvement, and areas which are not getting explored because of a lack of this solution.
Clarity on these points would ultimately help you make the best implementation decisions.
Data Source Identification
This stage requires a lot of homework into your current data handling process. Understanding the kind of data you have, where they are located, how they are collected, and used are just a few questions that you would have to find an answer to.
Analytics Tool Selection
After you have identified the sources of data, the next step would be finding the best analytics tool. While our previously covered section on types of IoT analytics platforms can come handy here, there might be an event where you’d need a platform that could handle and analyze multiple data types. In those instances the best bet would be to create a custom solution.
Analytics Infrastructure Development
With all your data sources and tools now streamlined, we can start building the analytics infrastructure. This would also involve a planned set up of hardware and software including data storage, cloud infrastructures, scalability features, and security systems.
Test and Validate
It is extremely critical to test all the functionalities, ensuring that they operate as intended. At this stage, our IoT developers tend to run analytical algorithms on a data subset to ensure that the insights it is generating are accurate. Additionally, we validate the system against regulatory and security microscopes to guarantee its market acceptance.
Deploy and Monitor
Once the analytics system has been tested and validated on both technical and user front, you can deploy the software in your solution. The key here is to continuously track performance and make necessary adjustments until your business objective is met.
Final Analysis
IoT analytics, while offering innumerable benefits to organizations looking to create a connected ecosystem, requires a fair amount of deliberation on the front of planning and implementation. The number one question that you as a business owner will have to answer is whether to go with a ready-made solution whose data security and integrations are not in your control, or build something personalized from the ground up.
The long-run cost benefit analysis will always favor investing in custom IoT software development services. But the decision lies with your budget and requirements.
We hope that the article gave you the insights you were looking for. If you find your business in need of a custom data analytics software, reach out to us.
FAQs
Q. What is IoT data analytics?
A. IoT analytics involves collecting, processing, and analyzing data generated by Internet of Things devices to extract valuable insights, optimize operations, and support decision-making.
Q. What are the key features of an IoT analytics software?
A. Key features of IoT analytics software include data collection and integration, real-time processing, advanced analytics (e.g., machine learning, predictive analytics), data visualization, scalability, security, and support for various IoT protocols and devices.
Q. What IoT analytics challenges should I expect?
A. Nothing if you partner with an IoT analytics company like Appinventiv. In other cases, the challenges can be around handling large volumes of data, ensuring data security and privacy, integrating diverse data sources, managing real-time data processing, and maintaining data quality and accuracy.

THE AUTHOR
Sudeep Srivastava
Co-Founder and Director