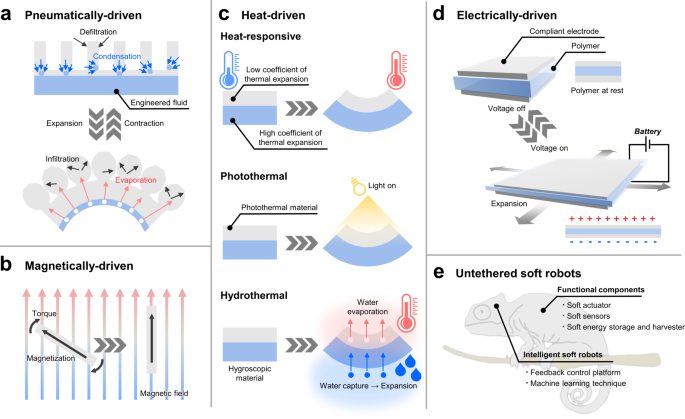
Untethered soft actuators for soft standalone robotics
Hawkes, E. W., Blumenschein, L. H., Greer, J. D. & Okamura, A. M. A soft robot that navigates its environment through growth. Sci. Robot. 2, eaan3028 (2017).
Justus, K. B. et al. A biosensing soft robot: autonomous parsing of chemical signals through integrated organic and inorganic interfaces. Sci. Robot. 4, eaax0765 (2019).
Hao, Y., Gao, J., Lv, Y. & Liu, J. Low melting point alloys enabled stiffness tunable advanced materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2201942 (2022).
Gao, M., Meng, Y., Shen, C. & Pei, Q. Stiffness variable polymers comprising phase‐changing side‐chains: material syntheses and application explorations. Adv. Mater. 34, 2109798 (2022).
Tetsuka, H., Pirrami, L., Wang, T., Demarchi, D. & Shin, S. R. Wirelessly powered 3D printed hierarchical biohybrid robots with multiscale mechanical properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2202674 (2022).
Nardekar, S. S. & Kim, S. J. Untethered magnetic soft robot with ultra‐flexible wirelessly rechargeable micro‐supercapacitor as an oboard power source. Adv. Sci. 10, 2303918 (2023).
Li, Y. et al. Multi‐degree‐of‐freedom robots powered and controlled by microwaves. Adv. Sci. 9, 2203305 (2022).
Iyer, V., Najafi, A., James, J., Fuller, S. & Gollakota, S. Wireless steerable vision for live insects and insect-scale robots. Sci. Robot. 5, eabb0839 (2020).
Yang, H. et al. Multifunctional metallic backbones for origami robotics with strain sensing and wireless communication capabilities. Sci. Robot. 4, eaax7020 (2019).
Ozaki, T., Ohta, N., Jimbo, T. & Hamaguchi, K. A wireless radiofrequency-powered insect-scale flapping-wing aerial vehicle. Nat. Electron. 4, 845–852 (2021).
Li, M., Pal, A., Aghakhani, A., Pena-Francesch, A. & Sitti, M. Soft actuators for real-world applications. Nat. Rev. Mater. 7, 235–249 (2022).
El-Atab, N. et al. Soft actuators for soft robotic applications: a review. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2, 2000128 (2020).
Guo, Y., Liu, L., Liu, Y. & Leng, J. Review of dielectric elastomer actuators and their applications in soft robots. Adv. Intell. Syst. 3, 2000282 (2021).
Rich, S. I., Wood, R. J. & Majidi, C. Untethered soft robotics. Nat. Electron. 1, 102–112 (2018).
Kim, H. et al. Shape morphing smart 3D actuator materials for micro soft robot. Mater. Today 41, 243–269 (2020).
Zhao, Y. et al. Physically intelligent autonomous soft robotic maze escaper. Sci. Adv. 9, eadi3254 (2023).
Ng, C. S. X. et al. Locomotion of miniature soft robots. Adv. Mater. 33, 2003558 (2021).
Li, G. et al. Self-powered soft robot in the mariana trench. Nature 591, 66–71 (2021).
Runciman, M., Darzi, A. & Mylonas, G. P. Soft robotics in minimally invasive surgery. Soft Robot. 6, 423–443 (2019).
Xu, S. et al. A dynamic electrically driven soft valve for control of soft hydraulic actuators. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 118, e2103198118 (2021).
Ge, L., Dong, L., Wang, D., Ge, Q. & Gu, G. A digital light processing 3D printer for fast and high-precision fabrication of soft pneumatic actuators. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 273, 285–292 (2018).
Li, H. et al. High-force soft pneumatic actuators based on novel casting method for robotic applications. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 306, 111957 (2020).
Bira, N., Mengüç, Y. & Davidson, J. R. In 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) (IEEE, 2020).
Acome, E. et al. Hydraulically amplified self-healing electrostatic actuators with muscle-like performance. Science 359, 61–65 (2018). This study presents muscle-mimetic soft actuators that harness electrostatic and hydraulic mechanism using liquid dielectric material.
Mitchell, S. K. et al. An easy‐to‐implement toolkit to create versatile and high‐performance HASEL actuators for untethered soft robots. Adv. Sci. 6, 1900178 (2019).
Zhang, Y. F. et al. Miniature pneumatic actuators for soft robots by high‐resolution multimaterial 3D printing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 4, 1900427 (2019).
Leroy, E., Hinchet, R. & Shea, H. Multimode hydraulically amplified electrostatic actuators for wearable haptics. Adv. Mater. 32, 2002564 (2020).
Bell, M. A., Gorissen, B., Bertoldi, K., Weaver, J. C. & Wood, R. J. A modular and self‐contained fluidic engine for soft actuators. Adv. Intell. Syst. 4, 2100094 (2022).
Zatopa, A., Walker, S. & Menguc, Y. Fully soft 3D-printed electroactive fluidic valve for soft hydraulic robots. Soft Robot. 5, 258–271 (2018).
Lin, Y., Xu, Y.-X. & Juang, J.-Y. Single-actuator soft robot for in-pipe crawling. Soft Robot. 10, 174–186 (2023).
Chee, P. S., Minjal, M. N., Leow, P. L. & Ali, M. S. M. Wireless powered thermo-pneumatic micropump using frequency-controlled heater. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 233, 1–8 (2015).
Han, J. et al. Untethered soft actuators by liquid–vapor phase transition: remote and programmable actuation. Adv. Intell. Syst. 1, 1900109 (2019).
Byun, J. et al. Underwater maneuvering of robotic sheets through buoyancy-mediated active flutter. Sci. Robot. 6, eabe0637 (2021).
Yoon, Y. et al. Bioinspired untethered soft robot with pumpless phase change soft actuators by bidirectional thermoelectrics. Chem. Eng. J. 451, 138794 (2023).
Lee, J. et al. Bioinspired soft robotic fish for wireless underwater control of gliding locomotion. Adv. Intell. Syst. 4, 2100271 (2022).
Kang, B., Lee, Y., Piao, T., Ding, Z. & Wang, W. D. Robotic soft swim bladder using liquid–vapor phase transition. Mater. Horiz. 8, 939–947 (2021).
Li, M. et al. Miniature coiled artificial muscle for wireless soft medical devices. Sci. Adv. 8, eabm5616 (2022).
Mirvakili, S. M., Sim, D., Hunter, I. W. & Langer, R. Actuation of untethered pneumatic artificial muscles and soft robots using magnetically induced liquid-to-gas phase transitions. Sci. Robot. 5, eaaz4239 (2020).
Tang, Y. et al. Wireless miniature magnetic phase‐change soft actuators. Adv. Mater. 34, 2204185 (2022).
Diteesawat, R. S., Helps, T., Taghavi, M. & Rossiter, J. Electro-pneumatic pumps for soft robotics. Sci. Robot. 6, eabc3721 (2021).
Matia, Y., An, H. S., Shepherd, R. F. & Lazarus, N. Magnetohydrodynamic levitation for high-performance flexible pumps. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 119, e2203116119 (2022).
Xu, S., Nunez, C. M., Souri, M. & Wood, R. J. A compact DEA-based soft peristaltic pump for power and control of fluidic robots. Sci. Robot. 8, eadd4649 (2023).
Feng, M., Yang, D., Majidi, C. & Gu, G. High‐speed and low‐energy actuation for pneumatic soft robots with internal exhaust air recirculation. Adv. Intell. Syst. 5, 2200257 (2023).
Tse, Y. A., Wong, K. W., Yang, Y. & Wang, M. Y. In 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (IEEE, 2020).
Sun, J., Zhou, D., Deng, J. & Liu, Y. Development of a high flow rate soft pump driven by intersected twisted artificial muscles units. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 70, 7153–7162 (2022).
Zhang, W. H., Qin, L., Wang, J. Y. & Xu, W. Design of squeezing-tube-driven pump for soft pneumatic robotics based on spiral spring winding. Appl. Phys. Letters 122, 093702 (2023).
Cacucciolo, V. et al. Stretchable pumps for soft machines. Nature 572, 516–519 (2019).
Tang, W. et al. Customizing a self-healing soft pump for robot. Nat. Commun. 12, 2247 (2021).
Qi, J., Gao, F., Sun, G., Yeo, J. C. & Lim, C. T. HaptGlove—untethered pneumatic glove for multimode haptic feedback in reality–virtuality continuum. Adv. Sci. 10, 2301044 (2023).
Lin, D., Yang, F., Gong, D. & Li, R. Bio-inspired magnetic-driven folded diaphragm for biomimetic robot. Nat. Commun. 14, 163 (2023).
Shao, Y. et al. 4D printing light-driven soft actuators based on liquid-vapor phase transition composites with inherent sensing capability. Chem. Eng. J. 454, 140271 (2023).
Fischer, P. & Ghosh, A. Magnetically actuated propulsion at low reynolds numbers: towards nanoscale control. Nanoscale 3, 557–563 (2011).
Brauer, J. R. Magnetic actuators and sensors 400,1-21 (John Wiley & Sons, 2006).
Nguyen, V. Q., Ahmed, A. S. & Ramanujan, R. V. Morphing soft magnetic composites. Adv. Mater. 24, 4041–4054 (2012).
Sitti, M. & Wiersma, D. S. Pros and cons: magnetic versus optical microrobots. Adv. Mater. 32, 1906766 (2020).
Singamaneni, S., Bliznyuk, V. N., Binek, C. & Tsymbal, E. Y. Magnetic nanoparticles: recent advances in synthesis, self-assembly and applications. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 16819–16845 (2011).
Ahn, C. H. & Allen, M. G. In Proceedings IEEE Micro Electro Mechanical Systems. 1995 408 (IEEE).
Howe, D. Magnetic actuators. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 81, 268–274 (2000).
Joyee, E. B. & Pan, Y. A fully three-dimensional printed inchworm-inspired soft robot with magnetic actuation. Soft Robot. 6, 333–345 (2019).
Kim, S., Hashi, S. & Ishiyama, K. Magnetic actuation based snake-like mechanism and locomotion driven by rotating magnetic field. IEEE Trans. Magn. 47, 3244–3247 (2011).
Peng, L. et al. Slug-inspired magnetic soft millirobot fully integrated with triboelectric nanogenerator for on‐board sensing and self‐powered charging. Nano energy 99, 107367 (2022).
Cui, J. et al. Nanomagnetic encoding of shape-morphing micromachines. Nature 575, 164–168 (2019).
Gu, H. et al. Magnetic cilia carpets with programmable metachronal waves. Nat. Commun. 11, 2637 (2020).
Al Khatib, E. et al. Magnetically actuated simple millirobots for complex navigation and modular assembly. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 5, 2958–2965 (2020).
Magdanz, V. et al. IRONSperm: Sperm-templated soft magnetic microrobots. Sci. Adv. 6, eaba5855 (2020).
Tang, D. et al. Origami-inspired magnetic-driven soft actuators with programmable designs and multiple applications. Nano Energy 89, 106424 (2021).
Mao, G. et al. Ultrafast small-scale soft electromagnetic robots. Nat. Commun. 13, 4456 (2022).
Kim, Y. & Zhao, X. Magnetic soft materials and robots. Chem. Rev. 122, 5317–5364 (2022).
Wang, L. et al. Reprogrammable, magnetically controlled polymeric nanocomposite actuators. Mater. Horiz. 5, 861–867 (2018).
Cao, X. et al. 3D printing magnetic actuators for biomimetic applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 30127–30136 (2021).
Paknahad, A. A. & Tahmasebipour, M. An electromagnetic micro-actuator with PDMS-Fe3O4 nanocomposite magnetic membrane. Microelectron. Eng. 216, 111031 (2019).
Han, B. et al. Reprogrammable soft robot actuation by synergistic magnetic and light fields. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2110997 (2022).
Song, H. et al. Reprogrammable ferromagnetic domains for reconfigurable soft magnetic actuators. Nano Lett. 20, 5185–5192 (2020).
Mahato, M. et al. A dual‐responsive magnetoactive and electro–ionic soft actuator derived from a nickel‐based metal–organic framework. Adv. Mater. 34, 2203613 (2022).
Liu, Y. et al. Responsive magnetic nanocomposites for intelligent shape-morphing microrobots. ACS nano 17, 8899–8917 (2023).
Zhou, H., Mayorga-Martinez, C. C., Pané, S., Zhang, L. & Pumera, M. Magnetically driven micro and nanorobots. Chem. Rev. 121, 4999–5041 (2021).
Quashie, D. et al. Magnetic bio-hybrid micro actuators. Nanoscale 14, 4364–4379 (2022).
Gao, Y., Wei, F., Chao, Y. & Yao, L. Bioinspired soft microrobots actuated by magnetic field. Biomed. Microdevices 23, 1–19 (2021).
Abdelaziz, M. & Habib, M. in 2020 21st International Conference on Research and Education in Mechatronics (REM). 1-6 (IEEE).
Gao, W. et al. Cargo‐towing fuel‐free magnetic nanoswimmers for targeted drug delivery. small 8, 460–467 (2012).
Tang, J. et al. Super‐soft and super‐elastic DNA robot with magnetically driven navigational locomotion for cell delivery in confined space. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 2490–2495 (2020).
Ju, Y. et al. Reconfigurable magnetic soft robots with multimodal locomotion. Nano Energy 87, 106169 (2021).
Huang, X. et al. Highly dynamic shape memory alloy actuator for fast moving soft robots. Adv. Mater. Technol. 4, 1800540 (2019).
Ishida, M. et al. Morphing structure for changing hydrodynamic characteristics of a soft underwater walking robot. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 4, 4163–4169 (2019).
Xie, H. et al. Reconfigurable magnetic microrobot swarm: multimode transformation, locomotion, and manipulation. Sci. Robot. 4, eaav8006 (2019).
Ha, M. et al. Reconfigurable magnetic origami actuators with on‐board sensing for guided assembly. Adv. Mater. 33, 2008751 (2021).
Wu, Y. et al. Locally controllable magnetic soft actuators with reprogrammable contraction-derived motions. Sci. Adv. 8, eabo6021 (2022).
Zhang, Y. et al. Reconfigurable magnetic liquid metal robot for high-performance droplet manipulation. Nano Lett. 22, 2923–2933 (2022).
Guitron, S., Guha, A., Li, S. & Rus, D. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 4807–4813 (IEEE, 2017).
Behrens, M. R. & Ruder, W. C. Smart magnetic microrobots learn to swim with deep reinforcement learning. Adv. Intell. Syst. 4, 2200023 (2022).
Cheng, Y. et al. A fast autonomous healing magnetic elastomer for instantly recoverable, modularly programmable, and thermorecyclable soft robots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2101825 (2021).
Lu, H., Hong, Y., Yang, Y., Yang, Z. & Shen, Y. Battery‐less soft millirobot that can move, sense, and communicate remotely by coupling the magnetic and piezoelectric effects. Adv. Sci. 7, 2000069 (2020).
Dong, Y. et al. Untethered small-scale magnetic soft robot with programmable magnetization and integrated multifunctional modules. Sci. Adv. 8, eabn8932 (2022).
Ebrahimi, N. et al. Magnetic actuation methods in bio/soft robotics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2005137 (2021).
Miriyev, A., Stack, K. & Lipson, H. Soft material for soft actuators. Nat. Commun. 8, 596 (2017).
Ula, S. W. et al. Liquid crystal elastomers: an introduction and review of emerging technologies. Liq. Cryst. Rev. 6, 78–107 (2018).
Küpfer, J. & Finkelmann, H. Nematic liquid single crystal elastomers. Die Makromol. Chem., Rapid Commun. 12, 717–726 (1991).
Fu, C., Xia, Z., Hurren, C., Nilghaz, A. & Wang, X. Textiles in soft robots: current progress and future trends. Biosens. Bioelectron. 196, 113690 (2022).
Xing, H., Li, J., Shi, Y., Guo, J. & Wei, J. Thermally driven photonic actuator based on silica opal photonic crystal with liquid crystal elastomer. ACS Appl. Mater. interfaces 8, 9440–9445 (2016).
Zhai, F. et al. 4D-printed untethered self-propelling soft robot with tactile perception: rolling, racing, and exploring. Matter 4, 3313–3326 (2021).
Wu, S., Hong, Y., Zhao, Y., Yin, J. & Zhu, Y. Caterpillar-inspired soft crawling robot with distributed programmable thermal actuation. Sci. Adv. 9, eadf8014 (2023).
Kotikian, A. et al. Untethered soft robotic matter with passive control of shape morphing and propulsion. Sci. Robot. 4, eaax7044 (2019).
He, Q. et al. Electrically controlled liquid crystal elastomer–based soft tubular actuator with multimodal actuation. Sci. Adv. 5, eaax5746 (2019).
Jiang, H., Li, C. & Huang, X. Actuators based on liquid crystalline elastomer materials. Nanoscale 5, 5225–5240 (2013).
Kim, T. H. et al. Biomimetic thermal-sensitive multi-transform actuator. Sci. Rep. 9, 7905 (2019).
Wang, H.-X. et al. Thermal-responsive hydrogel actuators with photo-programmable shapes and actuating trajectories. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 51244–51252 (2022).
Wei, W. et al. Recent advances and perspectives of shape memory polymer fibers. Er Poly. J. 175, 111385 (2022).
Lendlein, A. & Gould, O. E. Reprogrammable recovery and actuation behaviour of shape-memory polymers. Nat. Rev. Mater. 4, 116–133 (2019).
Yang, Y. et al. Enabling the sunlight driven response of thermally induced shape memory polymers by rewritable CH 3 NH 3 PbI 3 perovskite coating. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 7285–7290 (2017).
Chen, S., Zhang, Q. & Feng, J. 3D printing of tunable shape memory polymer blends. J. Mater. Chem. C. 5, 8361–8365 (2017).
Qian, S., Yao, S., Wang, Y., Yuan, L. & Yu, J. Harvesting low-grade heat by coupling regenerative shape-memory actuator and piezoelectric generator. Appl. Energy 322, 119462 (2022).
Knick, C. R., Smith, G. L., Morris, C. J. & Bruck, H. A. Rapid and low power laser actuation of sputter-deposited NiTi shape memory alloy (SMA) MEMS thermal bimorph actuators. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 291, 48–57 (2019).
Sun, J., Tighe, B., Liu, Y. & Zhao, J. Twisted-and-coiled actuators with free strokes enable soft robots with programmable motions. Soft Robot. 8, 213–225 (2021).
He, Q., Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Song, Z. & Cai, S. Recyclable and self-repairable fluid-driven liquid crystal elastomer actuator. ACS Appl. Mater. interfaces 12, 35464–35474 (2020).
Pan, M. et al. Soft actuators and robotic devices for rehabilitation and assistance. Adv. Intell. Syst. 4, 2100140 (2022).
Kanik, M. et al. Strain-programmable fiber-based artificial muscle. Science 365, 145–150 (2019).
Shen, Q. et al. A multiple-shape memory polymer-metal composite actuator capable of programmable control, creating complex 3D motion of bending, twisting, and oscillation. Sci. Rep. 6, 24462 (2016).
Wei, S. & Ghosh, T. K. Bioinspired structures for soft actuators. Adv. Mater. Technol. 7, 2101521 (2022).
Yang, Y., Wu, Y., Li, C., Yang, X. & Chen, W. Flexible actuators for soft robotics. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2, 1900077 (2020).
Yamada, M. et al. Photomobile polymer materials: towards light‐driven plastic motors. Angew. Chem. 120, 5064–5066 (2008).
Kumar, K. et al. A chaotic self-oscillating sunlight-driven polymer actuator. Nat. Commun. 7, 11975 (2016).
Yang, M. et al. Bioinspired phototropic MXene‐reinforced soft tubular actuators for omnidirectional light‐tracking and adaptive photovoltaics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2201884 (2022).
Hu, Z., Zhang, Y., Jiang, H. & Lv, J.-A. Bioinspired helical-artificial fibrous muscle structured tubular soft actuators. Sci. Adv. 9, eadh3350 (2023).
Wani, O. M., Zeng, H. & Priimagi, A. A light-driven artificial flytrap. Nat. Commun. 8, 15546 (2017).
Chen, Y. et al. Light-driven dandelion-inspired microfliers. Nat. Commun. 14, 3036 (2023).
He, Q. et al. Electrospun liquid crystal elastomer microfiber actuator. Sci. Robotics 6, eabi9704 (2021).
Wang, J., Zhao, T., Fan, Y., Wu, H. & Lv, J. A. Leveraging bioinspired structural constraints for tunable and programmable snapping dynamics in high‐speed soft actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2209798 (2023).
Kim, I. H. et al. Human-muscle-inspired single fibre actuator with reversible percolation. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 1198–1205 (2022).
Ionov, L. Biomimetic hydrogel‐based actuating systems. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 4555–4570 (2013).
Dawson, C., Vincent, J. F. & Rocca, A.-M. How pine cones open. Nature 390, 668–668 (1997).
Fratzl, P. & Barth, F. G. Biomaterial systems for mechanosensing and actuation. Nature 462, 442–448 (2009).
Le Duigou, A., Chabaud, G., Scarpa, F. & Castro, M. Bioinspired electro‐thermo‐hygro reversible shape‐changing materials by 4D printing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1903280 (2019).
Shin, B. et al. Hygrobot: A self-locomotive ratcheted actuator powered by environmental humidity. Sci. Robot. 3, eaar2629 (2018).
Zhang, F. et al. Unperceivable motion mimicking hygroscopic geometric reshaping of pine cones. Nat. Mater. 21, 1357–1365 (2022).
Aziz, S. et al. Plant‐like tropisms in artificial muscles. Adv. Mater. 35, e2212046 (2023).
Zhao, Z. et al. Actuation and locomotion driven by moisture in paper made with natural pollen. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 117, 8711–8718 (2020).
Yang, Z., An, Y., He, Y., Lian, X. & Wang, Y. A programmable actuator as synthetic earthworm. Adv. Mater. 35, 2303805 (2023).
Li, J., Mou, L., Liu, Z., Zhou, X. & Chen, Y. Oscillating light engine realized by photothermal solvent evaporation. Nat. Commun. 13, 5621 (2022).
Li, X. et al. Bioinspired multi‐stimuli responsive actuators with synergistic color‐and morphing‐change abilities. Adv. Sci. 8, 2101295 (2021).
Wu, Y., Dong, X., Kim, J. K., Wang, C. & Sitti, M. Wireless soft millirobots for climbing three-dimensional surfaces in confined spaces. Sci. Adv. 8, eabn3431 (2022).
Jeong, H., Lee, J., Kim, S., Moon, H. & Hong, S. Site-specific fabrication of a melanin-like pigment through spatially confined progressive assembly on an initiator-loaded template. Nat. Commun. 14, 3432 (2023).
Tang, W. et al. Self-contained soft electrofluidic actuators. Sci. Adv. 7, eabf8080 (2021).
Ha, J. H. et al. Electro-responsive hydrogel-based microfluidic actuator platform for photothermal therapy. Lab a Chip 20, 3354–3364 (2020).
Ji, X. et al. An autonomous untethered fast soft robotic insect driven by low-voltage dielectric elastomer actuators. Sci. Robot. 4, eaaz6451 (2019).
Rumley, E. H. et al. Biodegradable electrohydraulic actuators for sustainable soft robots. Sci. Adv. 9, eadf5551 (2023).
Yan, W. et al. Origami-based integration of robots that sense, decide, and respond. Nat. Commun. 14, 1553 (2023).
Chi, Y., Hong, Y., Zhao, Y., Li, Y. & Yin, J. Snapping for high-speed and high-efficient butterfly stroke–like soft swimmer. Sci. Adv. 8, eadd3788 (2022).
Li, T. et al. Fast-moving soft electronic fish. Sci. Adv. 3, e1602045 (2017).
Ankit et al. Soft actuator materials for electrically driven haptic interfaces. Adv. Intell. Syst. 4, 2100061 (2022).
Ni, D. et al. Polymer interdigitated pillar electrostatic (PIPE) actuators. Microsyst. nanoengineering 8, 18 (2022).
Xu, C., Faul, C. F., Taghavi, M. & Rossiter, J. Electric field‐driven dielectrophoretic elastomer actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2208943 (2023).
Zheng, Z. et al. Ionic shape-morphing microrobotic end-effectors for environmentally adaptive targeting, releasing, and sampling. Nat. Commun. 12, 411 (2021).
Fan, J., Wang, S., Yu, Q. & Zhu, Y. Swimming performance of the frog-inspired soft robot. Soft Robot. 7, 615–626 (2020).
Wang, D. et al. Dexterous electrical-driven soft robots with reconfigurable chiral-lattice foot design. Nat. Commun. 14, 5067 (2023).
Liang, J. et al. Electrostatic footpads enable agile insect-scale soft robots with trajectory control. Sci. Robot. 6, eabe7906 (2021).
Won, D. et al. Digital selective transformation and patterning of highly conductive hydrogel bioelectronics by laser-induced phase separation. Sci. Adv. 8, eabo3209 (2022).
Xiao, X. et al. An ultrathin rechargeable solid-state zinc ion fiber battery for electronic textiles. Sci. Adv. 7, eabl3742 (2021).
Dong, C. et al. 3D stretchable and self-encapsulated multimaterial triboelectric fibers. Sci. Adv. 8, eabo0869 (2022).
Sun, Z. et al. Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) enabled virtual shop applications using self‐powered sensor enhanced soft robotic manipulator. Adv. Sci. 8, 2100230 (2021).
Xue, P. et al. Highly conductive MXene/PEDOT: PSS‐integrated poly (N‐Isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels for bioinspired somatosensory soft actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2214867 (2023).
Lo, C.-Y. et al. Highly stretchable self-sensing actuator based on conductive photothermally-responsive hydrogel. Mater. Today 50, 35–43 (2021).
Dong, L. et al. Artificial neuromuscular fibers by multilayered coaxial integration with dynamic adaption. Sci. Adv. 8, eabq7703 (2022).
Zhou, J. et al. Breathable metal–organic framework enhanced humidity-responsive nanofiber actuator with autonomous triboelectric perceptivity. ACS nano 17, 17920–17930 (2023).
Kim, H. et al. Biomimetic chameleon soft robot with artificial crypsis and disruptive coloration skin. Nat. Commun. 12, 4658 (2021).
Yao, H. et al. Near–hysteresis-free soft tactile electronic skins for wearables and reliable machine learning. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 117, 25352–25359 (2020).
Shen, Z. et al. High‐stretchability, ultralow‐hysteresis conductingpolymer hydrogel strain sensors for soft machines. Adv. Mater. 34, 2203650 (2022).
Meng, X. et al. Hysteresis‐free nanoparticle‐reinforced hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 34, 2108243 (2022).
Su, X. et al. A highly conducting polymer for self‐healable, printable, and stretchable organic electrochemical transistor arrays and near hysteresis‐free soft tactile sensors. Adv. Mater. 34, 2200682 (2022).
Kim, K. K. et al. A deep-learned skin sensor decoding the epicentral human motions. Nat. Commun. 11, 2149 (2020).
Shu, S. et al. Machine‐learning assisted electronic skins capable of proprioception and exteroception in soft robotics. Adv. Mater. 35, 2211385 (2023).
Drotman, D., Jadhav, S., Sharp, D., Chan, C. & Tolley, M. T. Electronics-free pneumatic circuits for controlling soft-legged robots. Sci. Robot. 6, eaay2627 (2021).
Kim, J. et al. Reducing the metabolic rate of walking and running with a versatile, portable exosuit. Science 365, 668–672 (2019).
Schmitz, D. G. et al. Modulation of achilles tendon force with load carriage and exosuit assistance. Sci. Robot. 7, eabq1514 (2022).
Nuckols, R. W. et al. Individualization of exosuit assistance based on measured muscle dynamics during versatile walking. Sci. Robot. 6, eabj1362 (2021).
Georgarakis, A.-M., Xiloyannis, M., Wolf, P. & Riener, R. A textile exomuscle that assists the shoulder during functional movements for everyday life. Nat. Mach. Intell. 4, 574–582 (2022).
Proietti, T. et al. Restoring arm function with a soft robotic wearable for individuals with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 15, eadd1504 (2023).
Gu, H. et al. Self-folding soft-robotic chains with reconfigurable shapes and functionalities. Nat. Commun. 14, 1263 (2023).
Yi, S. et al. High-throughput fabrication of soft magneto-origami machines. Nat. Commun. 13, 4177 (2022).
Sitti, M. Physical intelligence as a new paradigm. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 46, 101340 (2021).
Zhang, J., Guo, Y., Hu, W. & Sitti, M. Wirelessly actuated thermo‐and magneto‐responsive soft bimorph materials with programmable shape‐morphing. Adv. Mater. 33, 2100336 (2021).
Zhao, Y. et al. Twisting for soft intelligent autonomous robot in unstructured environments. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 119, e2200265119 (2022).
Cheng, M. et al. Light‐fueled polymer film capable of directional crawling, friction‐controlled climbing, and self‐sustained motion on a human hair. Adv. Sci. 9, 2103090 (2022).
Cabanach, P. et al. Zwitterionic 3D‐printed non‐immunogenic stealth microrobots. Adv. Mater. 32, 2003013 (2020).
Sridhar, V. et al. Light-driven carbon nitride microswimmers with propulsion in biological and ionic media and responsive on-demand drug delivery. Sci. Robot. 7, eabm1421 (2022).
Shahsavan, H. et al. Bioinspired underwater locomotion of light-driven liquid crystal gels. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 117, 5125–5133 (2020).
Fu, L. et al. A humidity-powered soft robot with fast rolling locomotion. Research 9832901 https://doi.org/10.34133/2022/9832901 (2022).
Choi, M., Shin, B. & Kim, H.-Y. Hygromachines: Humidity-powered wheels, seesaws, and vehicles. Soft Robotics https://doi.org/10.1089/soro.2022.0218 (2023).
Ha, J. et al. Hygroresponsive coiling of seed awns and soft actuators. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 38, 100746 (2020).
Wang, R., Han, L., Wu, C., Dong, Y. & Zhao, X. Localizable, identifiable, and perceptive untethered light-driven soft crawling robot. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 6138–6147 (2022).
Zheng, Z. et al. Electrodeposited superhydrophilic‐superhydrophobic composites for untethered multi‐stimuli‐responsive soft millirobots. Adv. Sci. 10, 2302409 (2023).
Johnson, B. K. et al. Identification and control of a nonlinear soft actuator and sensor system. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 5, 3783–3790 (2020).
Lalegani Dezaki, M. & Bodaghi, M. Sustainable 4D printing of magneto-electroactive shape memory polymer composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 126, 35–48 (2023).
Dezaki, M. L. & Bodaghi, M. Shape memory meta-laminar jamming actuators fabricated by 4D printing. Soft Matter 19, 2186–2203 (2023).
Morin, S. A. et al. Camouflage and display for soft machines. Science 337, 828–832 (2012).