What Is Hybrid Cloud Security? How it Works & Best Practices
Hybrid cloud security is a framework for protecting data and applications in a computing environment that includes both private and public clouds. It combines on-premises and cloud-based resources to satisfy an organization’s diversified computing demands while ensuring strong security. This approach to cloud computing enables enterprises to benefit from the scalability and flexibility provided by public clouds while maintaining sensitive data within their own infrastructure.
As more businesses embrace hybrid cloud models to cater to their different computing demands, safeguarding the boundary between these environments has become critically important, making hybrid cloud security a top priority for ensuring protection, compliance, and resilience in an ever-changing digital ecosystem.
See our guides to public and private cloud security
How Hybrid Cloud Security Works
Hybrid cloud security combines on-premises controls and practices with cloud-specific solutions, reinforcing data and application protection between environments. Hybrid cloud security starts with analyzing and categorizing data and progresses to customized security measures. Hybrid cloud security generally follows best practices for network security and cloud security:
- Network segmentation decreases attack surfaces.
- Role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) regulate resource access.
- Encryption protects data both in transit and at rest.
- Continuous security monitoring identifies and responds to threats in real time.
- Data loss prevention (DLP) prevents unwanted data transfers.
- Firewalls and web application firewalls (WAFs) filter network traffic.
- Vulnerability assessment and management address system flaws and misconfigurations.
- Incident response strategies guarantee that breaches are managed and recovered from effectively.
- Compliance audits are conducted on a regular basis to ensure that requirements are met.
- Backup and disaster recovery procedures ensure that data is always available.
- Employee training increases understanding of optimal practices.
Hybrid Cloud Security Components
These components work together to establish a complete hybrid cloud security strategy, but the specific components and their configuration will vary depending on the organization’s security needs and the cloud services it employs.
- API Security: API security focuses on preventing unwanted access to application programming interfaces by establishing adequate authentication and authorization processes.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Data backup and disaster recovery plans assure data availability and business continuity in the event of data loss or service failures.
- Cloud-Native Security Features: Cloud-native security features, such as security groups, key management, and threat detection, are built-in tools and services provided by cloud providers to improve the security of cloud resources.
- Compliance and Audit Tools: Compliance and audit tools like GRC assist companies in adhering to applicable rules and industry standards by ensuring that security policies are followed and compliance is audited and documented.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP tools monitor and manage data flows in order to avoid illegal sharing or leaking of sensitive data.
- Encryption: Encrypting data and cloaking it in a secure, unreadable format both during transit (through protocols such as SSL/TLS) and at rest prevents unwanted access.
- Firewalls and Web Application Firewalls (WAF): Firewalls regulate network traffic and defend against external threats, whereas WAFs protect web applications by monitoring and filtering HTTP/HTTPS requests from potential threats.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM solutions control user access and permissions, ensuring that only authorized users and systems may interact with resources in both public and private clouds.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): IDS and IPS both monitor network traffic for signs of suspicious or malicious activity, with IDS identifying security risks and IPS actively preventing them.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an additional degree of protection by requiring users to give multiple kinds of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code texted to their mobile device.
- Network Segmentation: This is the process of partitioning your network into isolated segments, generally using firewalls and virtual LANs, in order to govern and protect traffic flow across public and private cloud environments.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM consolidates log data collecting, processing, and reporting from both cloud and on-premises systems, assisting in the detection and response to security events.
- User Training and Awareness Programs: These programs educate users and staff on best practices in security, training them to recognize and avoid common risks such as phishing.
- Vulnerability Management: This scans systems for vulnerabilities on a regular basis, prioritizing them based on risk profiles, and implementing fixes and updates to mitigate known security risks.
Hybrid Cloud Security Architecture Explained
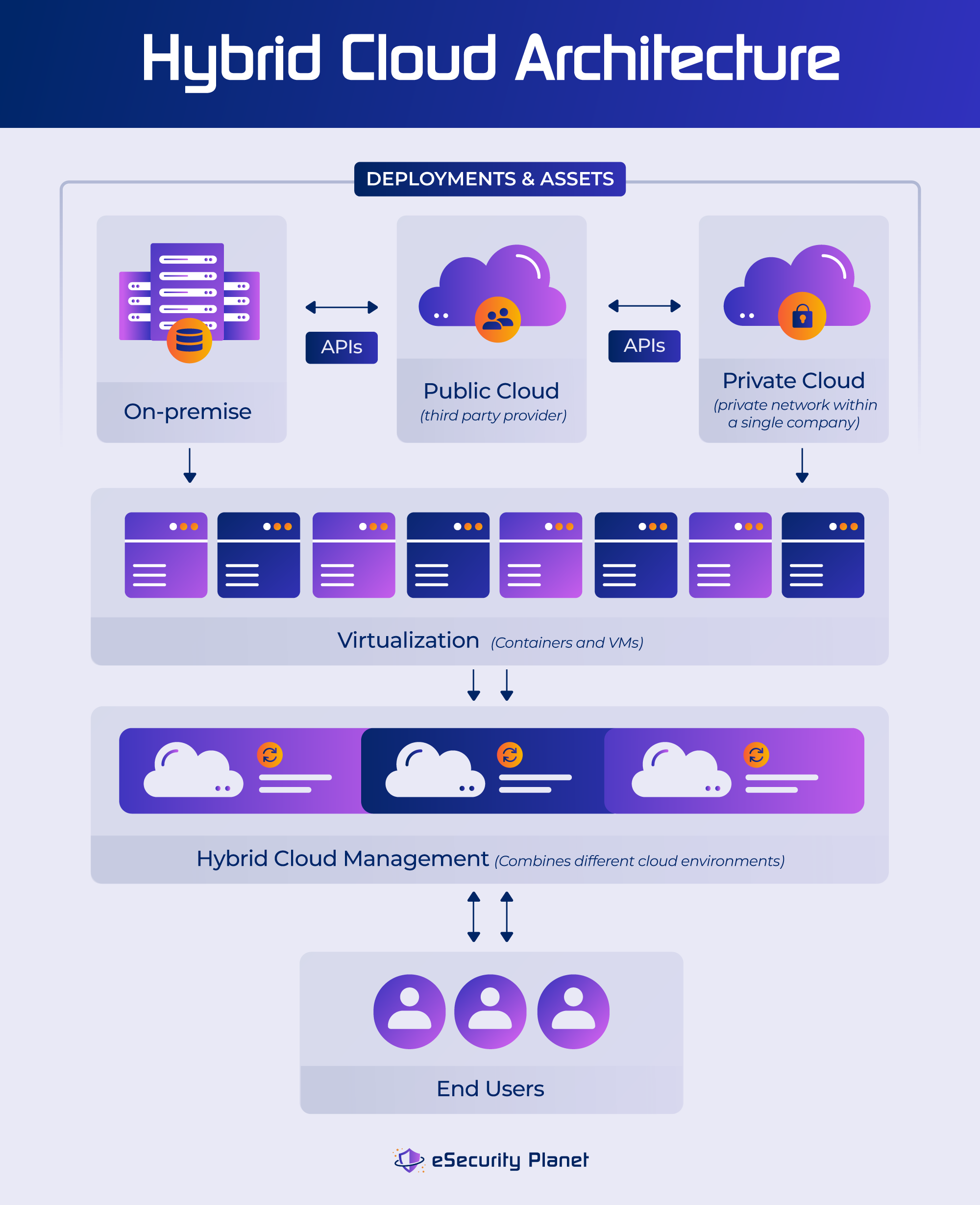
A hybrid cloud architecture primarily involves integrating different types of cloud and on-premises technology to fulfill an organization’s unique demands. Here are some examples of hybrid cloud security architectures.
Hybrid Cloud On-Premises
An enterprise in this case combines its on-premises data center or infrastructure with a public cloud. Some workloads, apps, or data may be hosted on the organization’s own servers, while others may be offloaded to a public cloud provider such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
Hybrid Cloud with a Public Cloud and Private Cloud
Here, businesses can combine a public cloud with a private cloud, which may be housed in a dedicated data center. They use the public cloud for some processes and services, but keep a private cloud for more sensitive data or mission-critical applications.
Complex Hybrid Cloud Environments
Businesses may mix various public cloud providers, private clouds, and on-premises technology in more complex setups. This enables them to select the most appropriate environment for each workload, application, or data type.
Data synchronization is critical in hybrid cloud architectures to provide consistency across infrastructures. Connecting private clouds, legacy systems, and public clouds through the internet or private networks guarantees that data and applications flow seamlessly. A single management tool facilitates supervision because managing numerous cloud environments independently can be complicated due to differences in APIs, SLAs, and features from different providers. This provides a centralized interface for effective control and monitoring of hybrid cloud resources.
6 Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Security
A hybrid cloud infrastructure gives enterprises a scalable, adaptable, and cost-effective solution that prioritizes data protection, privacy, and disaster recovery. This approach ensures business continuity and adaptation to changing demands by allowing for smooth resource allocation and cost control.
1. Flexibility
Hybrid clouds offer flexibility for enterprises with a wide range of demands and endpoints. They enable you to effortlessly move between on-premises and cloud servers based on your needs. You may manage your infrastructure at your own speed and respond quickly to changing demands.
2. Expense Management
It can be expensive to set up and manage on-premises data centers. By transferring resource-intensive activities to the cloud, a hybrid cloud approach can allow for cost-effective solutions. Cloud companies charge depending on consumption, which can lower infrastructure and maintenance costs, particularly for companies trying to meet fluctuating demand. Real-time monitoring and clear payment alternatives help with expenditure control.
3. Agile and Scalable Solutions
Hybrid architecture is extremely scalable, allowing for company expansion by adding or deleting cloud servers as required. Employees may connect to the office system using a variety of devices without the need for extra hardware. Depending on demand, operations can be scaled up or down to optimize expenses.
4. Data Control and Privacy
Large amounts of data may be stored and analyzed in the cloud. To guard against cyber attacks, cloud systems include powerful security features such as encryption, firewalls, authentication, and data backups. Data security is improved by privacy features like number masking and dynamic caller IDs. Hybrid solutions enable you to preserve sensitive data on private clouds while keeping general data on public servers.
5. Cloud Bursting
“Cloud bursting” allows workloads to be expanded to a public cloud during demand surges and then scaled down to the original server. This rented resource solution saves money and time while adjusting to changing workloads.
6. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
If security, privacy and regional compliance demands are met, storing or backing up critical data on cloud servers improves disaster recovery capability. Multiple backups provide data management even in the face of unforeseen occurrences like natural catastrophes. Because cloud-based operations can be expanded and controlled from anywhere, they provide business continuity in crisis scenarios.
5 Hybrid Cloud Security Challenges
When compared to typical security methods, securing a hybrid cloud environment brings unique challenges, particularly for enterprises with stringent regulatory requirements and established procedures. Some areas of concern include:
1. Shared Security Responsibility
It is important to understand the shared responsibility of your company and cloud service providers. Cloud providers protect the infrastructure, but clients must protect their data and applications.
How to address this challenge: To protect data and applications, ensure that providers can satisfy regulatory requirements and incorporate business continuity and disaster recovery strategies in service level agreements (SLAs). And keep tight controls on access and other frequent cloud security mistakes.
2. Incident Handling
When issues develop within the infrastructure of a cloud service provider, teamwork is required to resolve them. Issues such as data commingling in multicloud systems, data privacy influencing log analysis, and disparities in defining what constitutes an event can all provide difficulties.
How to address this challenge: To reduce downtime and data exposure, enterprises should define explicit incident response plans, including communication methods, and verify they comply with the cloud provider’s policies.
3. Application Security
Cloud applications are vulnerable to a variety of security risks, and a range of products address certain areas of this issue, such as software development life cycle security, authentication, compliance, monitoring, and risk management. Managing them separately can be difficult logistically, so look for solutions that incorporate various security roles.
How to address this challenge: Organizations should take a DevSecOps approach to security, including it in the application development lifecycle. Using automated security testing tools and doing frequent code reviews helps to protect the integrity of apps.
4. Data Protection
Because sensitive data is dispersed across several environments in hybrid cloud security, consistent security procedures and monitoring are required to prevent exposure and breaches.
How to address this challenge: Using a data-centric security approach, such as data encryption, data classification, access restrictions, and data loss prevention solutions, may help protect sensitive information no matter where it is stored.
5. Compliance and Auditing
Because of the requirement to follow varying standards across numerous cloud environments, compliance and auditing pose issues in hybrid cloud security, demanding complicated monitoring, reporting, and adherence processes.
How to address this challenge: To ease the compliance process, organizations should establish a centralized compliance and auditing system that uses automated technologies to monitor and report on the compliance status of their hybrid cloud environment.
Best Practices & Guidelines for Maximizing Hybrid Cloud Security
While specific configurations may differ, adopting these best practices assists businesses in mitigating risks and successfully responding to security challenges.
Encrypt and Inspect Traffic
Encrypting data in transit and then examining it guarantees that sensitive information is kept private during transmission while also allowing for the discovery of any possible security risks or breaches. This way, security is ensured on both ends.
Monitor and Audit Configurations
Continuous configuration monitoring and auditing aid in detecting deviations from defined security standards and policies, ensuring that the hybrid cloud system stays compliant and safe. Monitor and audit settings across all of your clouds and data centers on a regular basis. Misconfigurations, which are frequently the consequence of human mistakes, are a major source of vulnerabilities. Automation is a useful technique for ensuring secure setups.
Perform Vulnerability Scans
Vulnerability scans uncover possible flaws in the system, allowing for quick correction to strengthen security against hostile actors. Conduct vulnerability checks on a regular basis to uncover weak places in your infrastructure. Make use of automated solutions that prioritize vulnerabilities based on risk profiles to ensure efficient and successful remediation.
Apply Security Patches
Applying security updates on a regular basis keeps software and systems up to date, addressing known vulnerabilities and improving the hybrid cloud infrastructure’s security posture. By shortening the period between patch release and implementation, the window of opportunity for possible cyber attacks is reduced.
Enforce Zero Trust Security
To reduce the danger of unauthorized access or lateral movement by attackers, zero trust security necessitates strong authentication and access rules that regard all users and devices as untrusted entities. Implement security principles based on zero trust, which prioritize least-privilege access and strong authentication.
Have a Recovery Plan
Create an effective response strategy in the event of a security compromise. In the case of a security breach or disaster, a recovery plan specifies how to restore services and data while minimizing downtime and data loss and guaranteeing business continuity. Keeping backup storage separate from the original data source reduces the chance of a single point of failure and speeds up remediation operations.
Secure Endpoints
Endpoint security solutions, such as EDR and multi-factor authentication, prevent illegal access and data breaches by securing endpoints such as devices and user access points. While cloud computing has revolutionized company security, endpoints could still remain a weak link. It is critical to protect data going through and between these devices.
Top 3 Hybrid Cloud Security Vendors
The hybrid cloud security landscape is continuously expanding, and several major companies now offer comprehensive solutions to protect your data and apps in hybrid environments. Here are three of the top hybrid cloud security solutions to consider.

1. Acronis
Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud specializes in providing comprehensive services to safeguard data across various environments, particularly in hybrid cloud setups, making it a good option for organizations seeking to secure and manage their data in complex, multi-cloud, and on-premises environments.
Key Features: Acronis includes AI-based antivirus, anti-malware, and anti-ransomware technologies for proactive threat prevention, as well as fail-safe patching, forensic backup, and continuous data protection.
Services: Data backup and recovery, cybersecurity tools against malware, ransomware, and other threats, and services for data storage and management.
Unique Offering: AI-Based Protection, blockchain technology, and integrated data protection.

2. Skyhigh Security
Skyhigh’s Cloud Native Application Protection Platform offers an all-in-one solution for securing cloud-native applications, encompassing a risk-based perspective on application and data context.
Key Features: Skyhigh’s CNAPP examines workloads, data, and infrastructure in real time, detecting misconfigurations, software vulnerabilities, and sensitive data. For comprehensive security, it defends against configuration deviations, automates assessments, and supports short-lived workloads with application allow-listing, workload reinforcement, integrity monitoring, and On-Premises Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Scanning.
Services: Offers a unified set of controls based on an integrated platform, customer assistance, and expert guidance.
Unique Offering: Skyhigh (formerly McAfee MVISION) is a pioneering platform that integrates application and data context, combining Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) for public cloud infrastructure and Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) for application protection across virtual machines, compute instances, and containers.

3. Trend Micro Cloud One
Trend Micro Cloud One platform has broad support across public cloud providers (AWS, Google Cloud, Azure), VMware-based private clouds, and on-premises storage.
Key Features: Trend Micro offers AI and ML-powered vulnerability analysis, a bug bounty program for zero-day attack readiness, contributions from 15 global research centers, managed detection and response services, protection for cloud-native applications, and versatile integrations via native APIs. Advanced automation enhances vulnerability detection and compliance monitoring.
Services: Managed detection and response, threat analysis, and professional assistance are all available through the platform.
Unique Offering: Provides full coverage, including open source assets, filling a critical cybersecurity gap. Trend Micro’s relationship with Snyk offers specific coverage for open source assets, making it a good option for businesses that already rely on open source.
Bottom Line: Enhance Your Security Through Hybrid Cloud
Businesses should explore hybrid clouds if they have dynamic workloads, seasonal swings, need gradual cloud adoption, or want flexibility in the face of an uncertain future. Hybrid clouds allow businesses to adapt at their own speed, giving financial relief and a safety net for those hesitant to embrace full-scale changes. Hybrid cloud security, which combines traditional on-premises security practices with cloud-specific measures, ensures a comprehensive defense strategy, allowing organizations to benefit from cloud computing while effectively safeguarding their data and applications from evolving cyber threats and regulatory compliance issues.
Featured Partners: Cybersecurity Software
Read next:



